Figure 5.
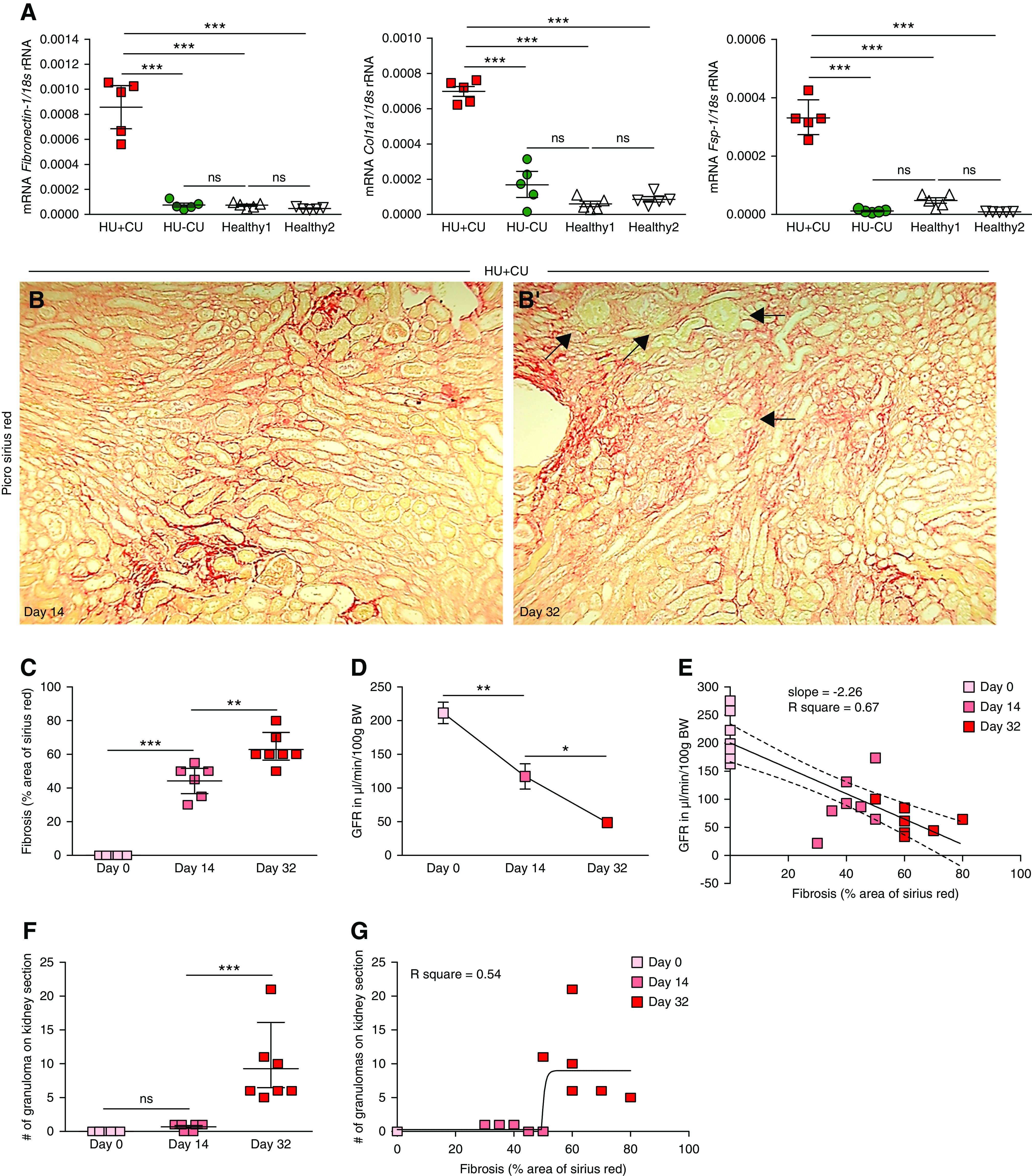
Renal UA crystal granulomas formed after interstitial fibrosis was established. Alb-creERT2;Glut9lox/lox and Glut9lox/lox control mice were injected intraperitoneally with tamoxifen. Both groups were fed either an acidogenic diet enriched with inosine or a standard chow diet with inosine for 32 days. (A) Intrarenal mRNA expression levels of the fibrosis marker Fibronectin 1, collagen (Col)1α1, and Fsp-1 of all four groups of mice (n=5 mice per group, one-way ANOVA). (B) Picro-sirius red staining illustrating interstitial fibrosis in kidney sections of HU−CU mice on days 14 (B) and 32 (B’). Black arrows point at UA granulomas. Magnification, ×200. (C) Quantification of Picro-sirius red–stained kidney sections from HU+CU mice (n=5–7 mice per group, one-way ANOVA). (D) GFR of HU+CU mice on days 0, 14, and 32 (n=5–7 mice per group, one-way ANOVA). (E) Linear regression analysis between GFR and fibrosis of mice with HU+CU over time (r2=0.67). (F) Number of UA granulomas counted on PAS-stained kidney sections from HU+CU mice on days 0, 14, and 32 (n=5–7 mice per group, one-way ANOVA). (G) Illustration of a nonlinear regression with curve fit between the number of granulomas per kidney section and the extent of interstitial fibrosis (r2=0.54). Data are mean±SD. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001; NS, not significant.
