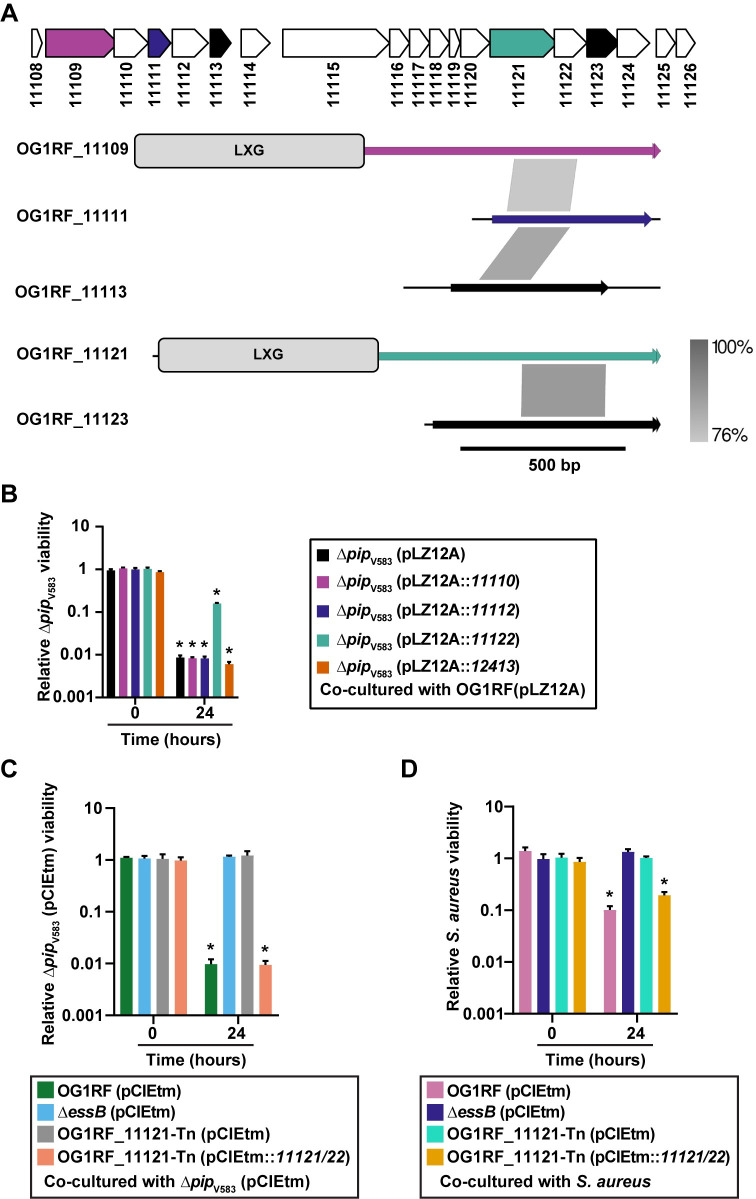
Fig 2. Identification of E. faecalis T7SS toxin and immunity proteins that dictate bystander growth inhibition.
(A) Putative toxin-encoding genes in the OG1RF T7SS locus. LXG domains in OG1RF_11109 and OG1RF_11121 were identified using KEGG and ExPASy PROSITE. Putative orphan toxins were identified by homology to OG1RF_11109 or OG1RF_11121. Gray lines between diagrams indicate the regions and degree of nucleotide conservation between genes. Homology diagrams were rendered in EasyFig. Gene colors for OG1RF_11109, OG1RF_11111, and OG1RF_11121 match the color scheme in panel (B). OG1RF_11113 and OG1RF_11123 are shaded black to indicate that their corresponding immunity genes were not tested in panel (B). (B) E. faecalis OG1RF T7SS mediated growth inhibition of phage resistant E. faecalis ΔpipV583 during infection is alleviated by expressing OG1RF_11122 in E. faecalis ΔpipV583 but not in the presence of pLZ12A empty vector, or expressing OG1RF_11110, OG1RF_11112, or OG1RF_12413. (C–D) Disruption of OG1RF_11121 by a transposon insertion rescues growth of phage resistant E. faecalis ΔpipV583 (C) and S. aureus (D) strains during co-culture. Complementation of OG1RF_11121-Tn restores bystander intoxication. Data represent three biological replicates. Error bars indicate standard deviation. *P < 0.0001 by unpaired Student’s t-test.