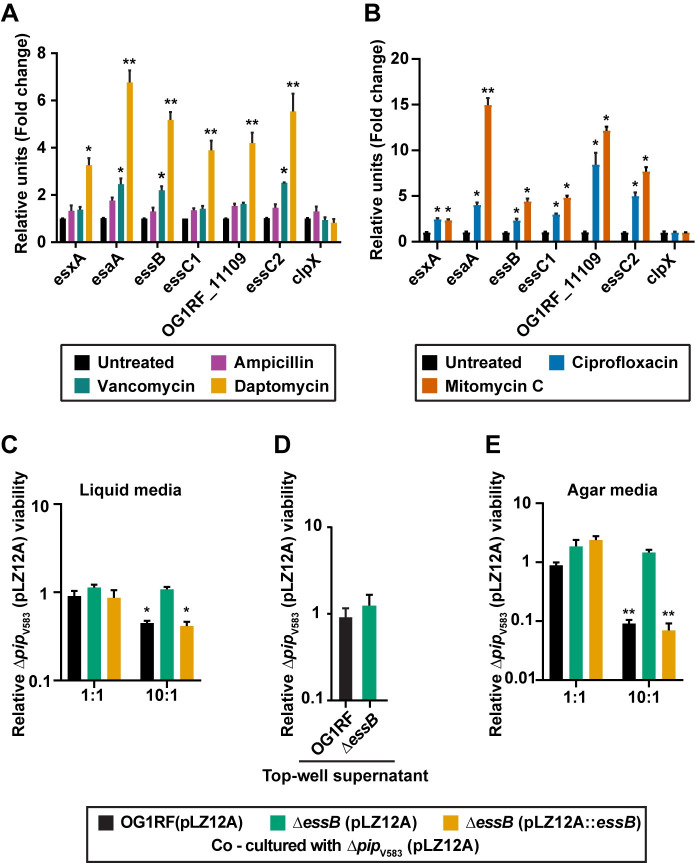
Fig 3. Sub-lethal antibiotic treatment enhances T7SS gene expression leading to inhibition of bystander bacteria.
Altered expression of T7SS genes upon exposure to sub-inhibitory concentrations of (A) ampicillin (0.19 μg/ml), vancomycin (0.78 μg/ml) or daptomycin (6.25 μg/ml) and (B) ciprofloxacin (2 μg/ml) or mitomycin C (4 μg/ml) for 40 minutes relative to the untreated control. clpX is shown as a negative control. (C-E) Contact–dependent T7SS mediated inhibition of bystander bacteria in the presence of daptomycin. Relative viability of E. faecalis ΔpipV583 was measured during co-culture with E. faecalis OG1RF or ΔessB antagonists in the presence and absence of daptomycin treatment in (C) liquid culture (2.5 μg/ml daptomycin), (D) trans-well plates to prevent physical engagement between cells (2.5 μg/ml daptomycin) and (E) in contact on agar media (0.5 μg/ml daptomycin). ΔessB (pLZ12A) and ΔessB (pLZ12A::essB) represent the empty vector control and complemented strains. Data show three biological replicates. Error bars indicate standard deviation. *P < 0.01, **P < 0.001 to 0.0001 by unpaired Student’s t-test.