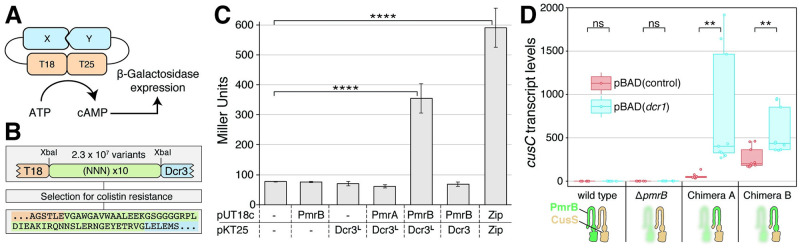
Fig 3. Dcr peptides interact with and activate PmrB.
(A) Schematic representation of the bacterial two-hybrid system. Binding of X to Y causes co-localization of T18 and T25 and production of cyclic AMP (cAMP) that subsequently increases ß-galactosidase expression. (B) Schematic representation of the constructed linker library and the functional linker that was selected. (C) ß-galactosidase assays using various fusion constructs with T18 expressed from pUT18c and T25 expressed from pKT25. T18 or T25 without an additional fusion were used as negative controls. Zip-fusions, which contain leucine zipper motifs that are known to dimerize, were used as a positive control. pKT25-Dcr3 lost the ability to provide colistin resistance, while the variant containing the selected linker pKT25-Dcr3L regained functionality. Each value represents the mean of six independent experiments. Error bars show the standard deviation. Asterisks indicate significant differences in ß-galactosidase activity (**** = p < 0.0001, t-test). (D) Relative transcript levels of cusC in E. coli MG1655 wild type, ΔpmrB and two chimeric CusS variants in a ΔpmrB mutant expressing Dcr1 or an empty control plasmid. The chimeric sensor kinases consist of the CusS scaffold where either the transmembrane and periplasmic domain (Chimera-A) or additionally the HAMP domain (Chimera-B) were replaced with the PmrB homologous parts. The box plots show transcript levels of cusC determined from a minimum of three biological and three technical replicates each. The horizontal line represents the median, the box represents the upper (Q3) and lower quartile (Q1) and the vertical lines represent the highest and lowest value. Asterisks indicate significant differences in transcript level (** = p < 0.01, t-test).