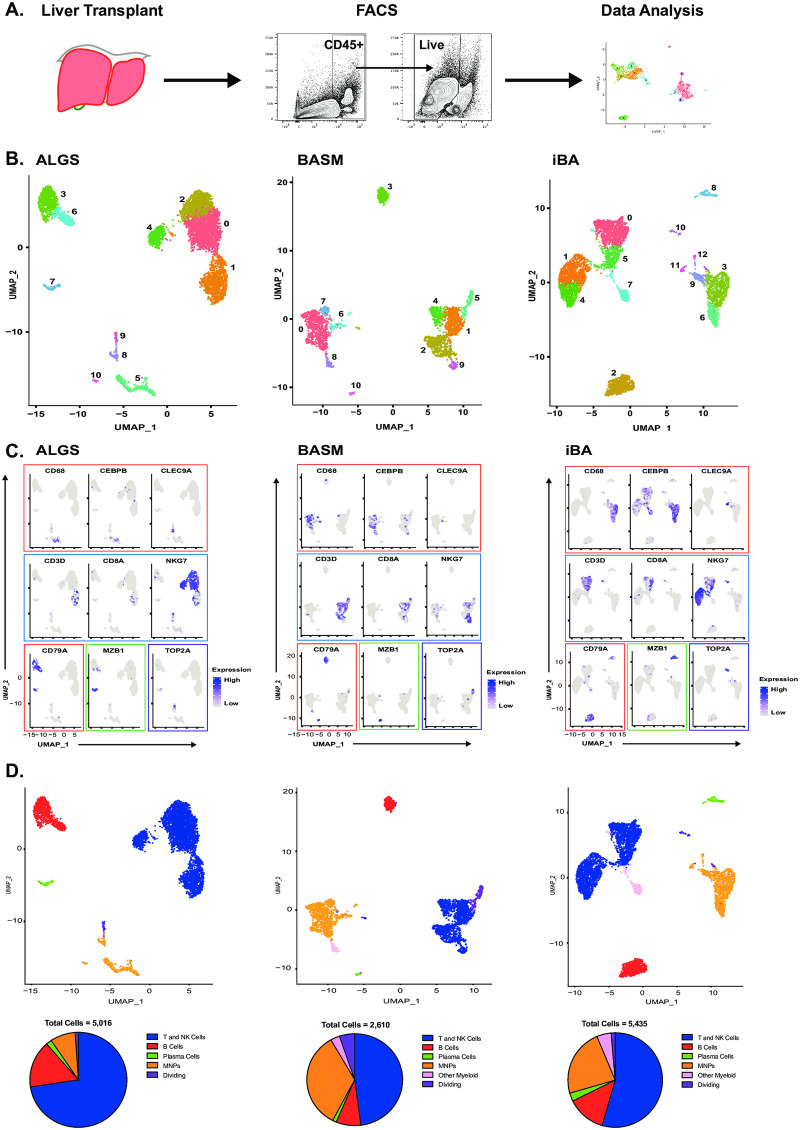
Fig 2. Single-cell RNA-seq enables immune cell characterization in cholestatic liver disease.
Hepatic CD45+ cells were isolated from liver tissue at the time of liver transplantation by fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS) for single-cell RNA-seq (scRNA-seq) analysis (A). UMAP of scRNA-seq data showing 11 clusters in ALGS (left) and BASM (middle) and 13 clusters in iBA (right) patient samples (B). Clusters were assigned to cell types based on the expression of lineage-specific genes (blue = T/NK cells; red = B cells; green = plasma cells; orange = MNP; pink = other myeloid cells; purple = dividing cells) in ALGS, BASM, and iBA (left to right) (C). UMAPs were re-colored by cell type and proportion of immune cells demonstrates greater numbers of MNP cells in BASM (middle) as compared to ALGS (right) and iBA (right) (D).