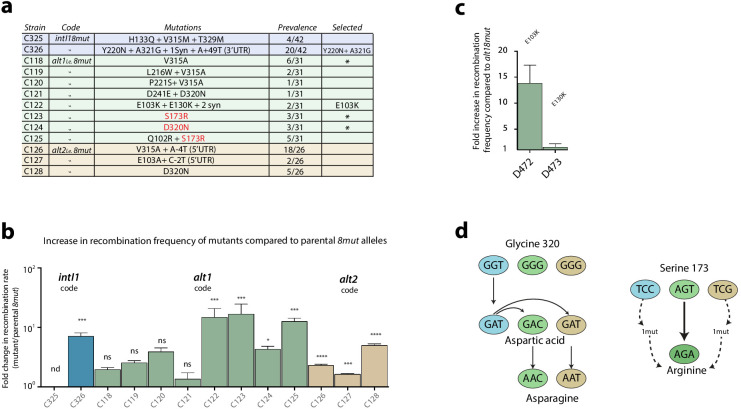
Figure 4. Second round of mutagenesis and enrichment cycles.
a: list of mutations found among the three 8mut alleles after four cycles. Substitutions that are not reachable from the intI18mut code are highlighted in red. b: fold increase in recombination rates for the attI x attI reaction of all mutants compared to their parental 8mut allele. Bars represent average values of at least three independent experiments. Error bars show standard error. Statistically significant results are indicated by * (alpha = 0.05). c: Analysis of the mutations found in the alt18mut mutant C122. Of both non-synonymous mutations, only E103K produces a relevant increase in activity. d: Mutational pathways in our experiments highlight the importance of broad sequence space exploration. Mutation S173R, conferring a high activity gain, was only found in the alt1 code because intI1 and alt2 codes needed an additional mutation to access that codon. Glycine to aspartic acid substitution (G320D) appeared in the intI allele in the first round of experiments and was included in both alt8mut alleles using two different codons. It then re-evolved to asparagine (D320N), a residue that was not reachable from any of the starting codons with a single mutation.