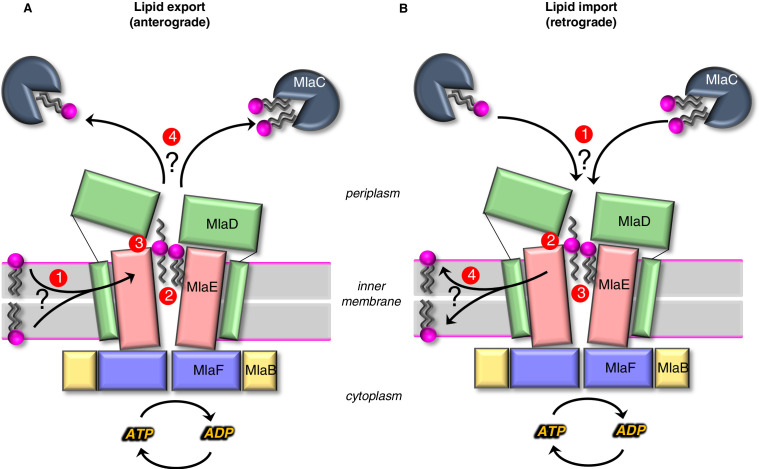
Figure 6. Models for lipid transport by MlaFEDB.
(A) Lipid export model: (1) Lipids are extracted from the IM and transferred to the outward-open pocket by an unknown mechanism. (2) Lipids are reoriented, from ‘tails-down’ to ‘extended’ or ‘tails-up’ configuration. (3) Conformational changes in MlaE coupled to the ATP hydrolysis cycle likely push lipids out of the MlaE pocket and into MlaD pore. (4) Lipids are transferred to MlaC to be shuttled across periplasm to the outer membrane MlaA-OmpC/F complex. MlaC may accommodate one or two phospholipids, or a single larger lipid. (B) Lipid import model: (1) Lipids from MlaC are transferred to MlaD, likely dependent on ATP-driven conformational changes in MlaD and MlaE. (2) Lipids travel through the continuous channel from MlaD and are transferred to the outward-open pocket of MlaE. (3) Phospholipids are reoriented ‘tails-down’, as they are transported between MlaD and MlaE. (4) Lipids are inserted into the inner membrane.