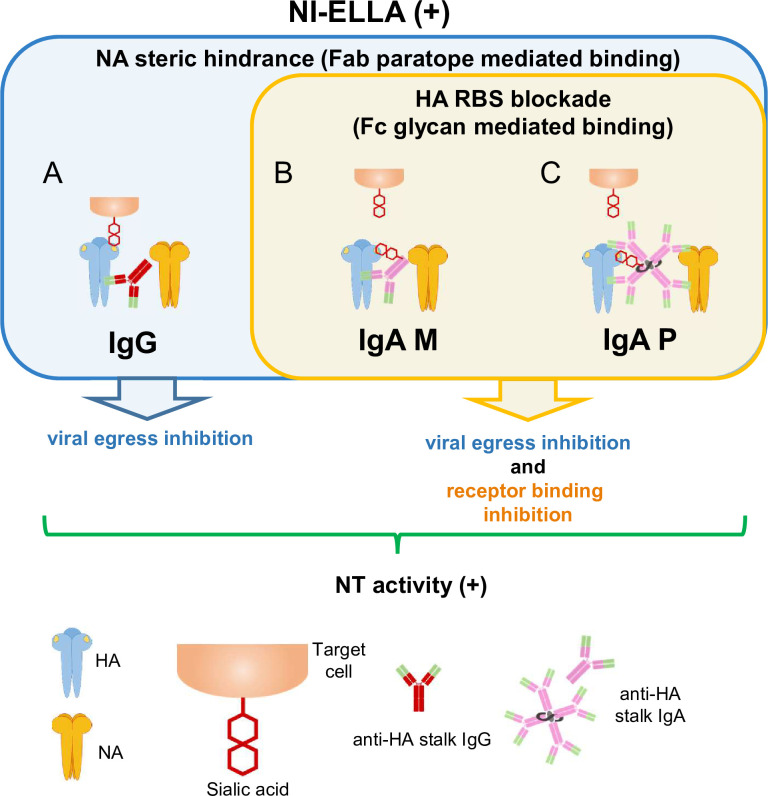
Fig 5. Summary of the mechanisms underlying anti-viral activity mediated by anti-HA stalk antibodies.
Different modes of interaction among anti-HA stalk antibodies, NA, and HA molecules that confer anti-viral activity (including NI activity) detected in the NI-ELLA. These interactions mediate NI activity via two binding modes between antibodies and HA: Fab paratope-mediated binding to the HA stalk and Fc glycan-mediated binding to the HA head. (A) In the case of anti-HA stalk-binding IgG antibodies, Fab paratope-mediated binding to the HA stalk will cause steric hindrance of neighboring NA molecules and inhibit viral egress, leading to NT activity. (B and C) In the case of HA stalk-targeting IgA antibodies, Fc glycan-mediated binding will cause HI activity due to blockade of the receptor binding site on HA, thereby inhibiting binding of sialic acid to the receptor binding site. In these interaction modes, simultaneous steric hindrance of neighboring NA molecules and blockade of the receptor binding site may also occur, leading to inhibition of both viral egress and receptor binding.