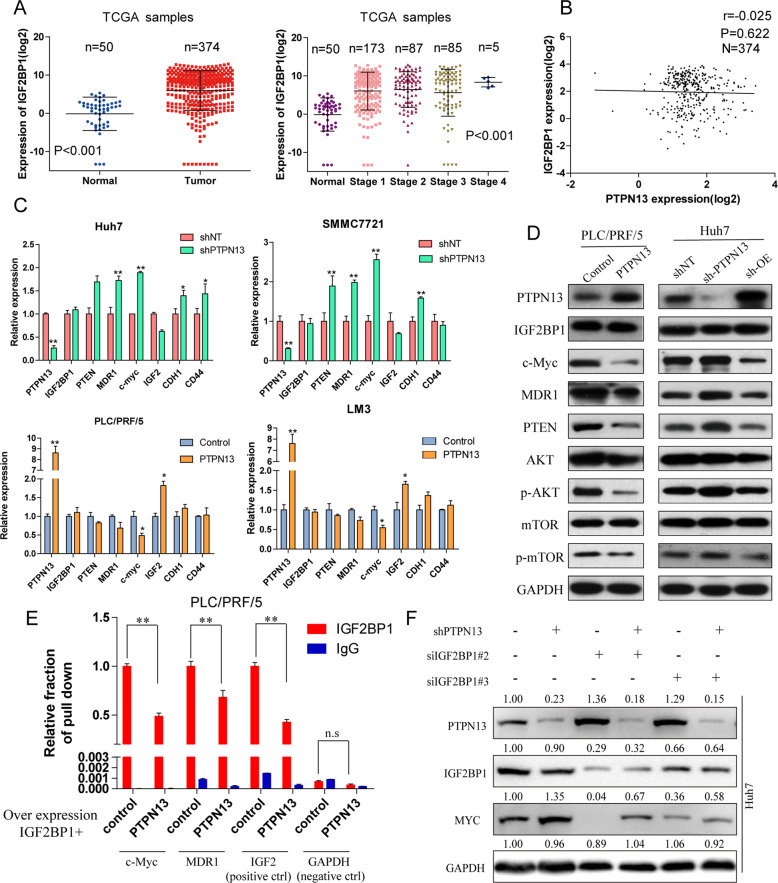
Fig. 6. PTPN13 inhibits IGF2BP1 activity to protect target mRNA levels and especially attenuates c-Myc accumulation.
A The expression levels of IGF2BP1 in 374 HCC tissues and 50 adjacent nontumor liver tissues in the TCGA cohort were analyzed by a t-test. Data are shown after a log2 transformation. B The correlation between PTPN13 and IGF2BP1 expression in 374 HCC tissue samples. Correlations were then analyzed by Pearson’s correlation analysis. C The effects of transient PTPN13 overexpression and a control vector in PLC/PRF/5 and LM3 cells and PTPN13 knockdown with shRNA and a control shRNA in Huh7 and SMMC-7721 cells on the mRNA expression of IGF2BP1 downstream genes are shown. D Immunoblot analysis of genes downstream of IGF2BP1 and relevant pathways related to cancer proliferation and metastasis (c-Myc, MDR1, PTEN, p-AKT, and p-mTOR) in PLC/PRF/5 and LM3 cells with transient PTPN13 overexpression and a control vector and Huh7 and SMMC-7721 cells with knockdown and control shRNA. E A RIP assay was performed using anti-IGF2BP1 and control IgG antibodies after transient PTPN13 overexpression, followed by qRT-PCR to examine the enrichment of c-Myc, MDR1, IGF2, and GAPDH. IGF2 served as a positive control, while GAPDH served as a negative control. F Immunoblot analysis of c-Myc expression in HCC cells expressing PTPN13-specific shRNAs or control cells with or without the transient transfection of IGF2BP1-specific siRNAs. Data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; ns not significant).