Fig. 1. The tissue and cellular potency of an ADC payload must be matched to delivery.
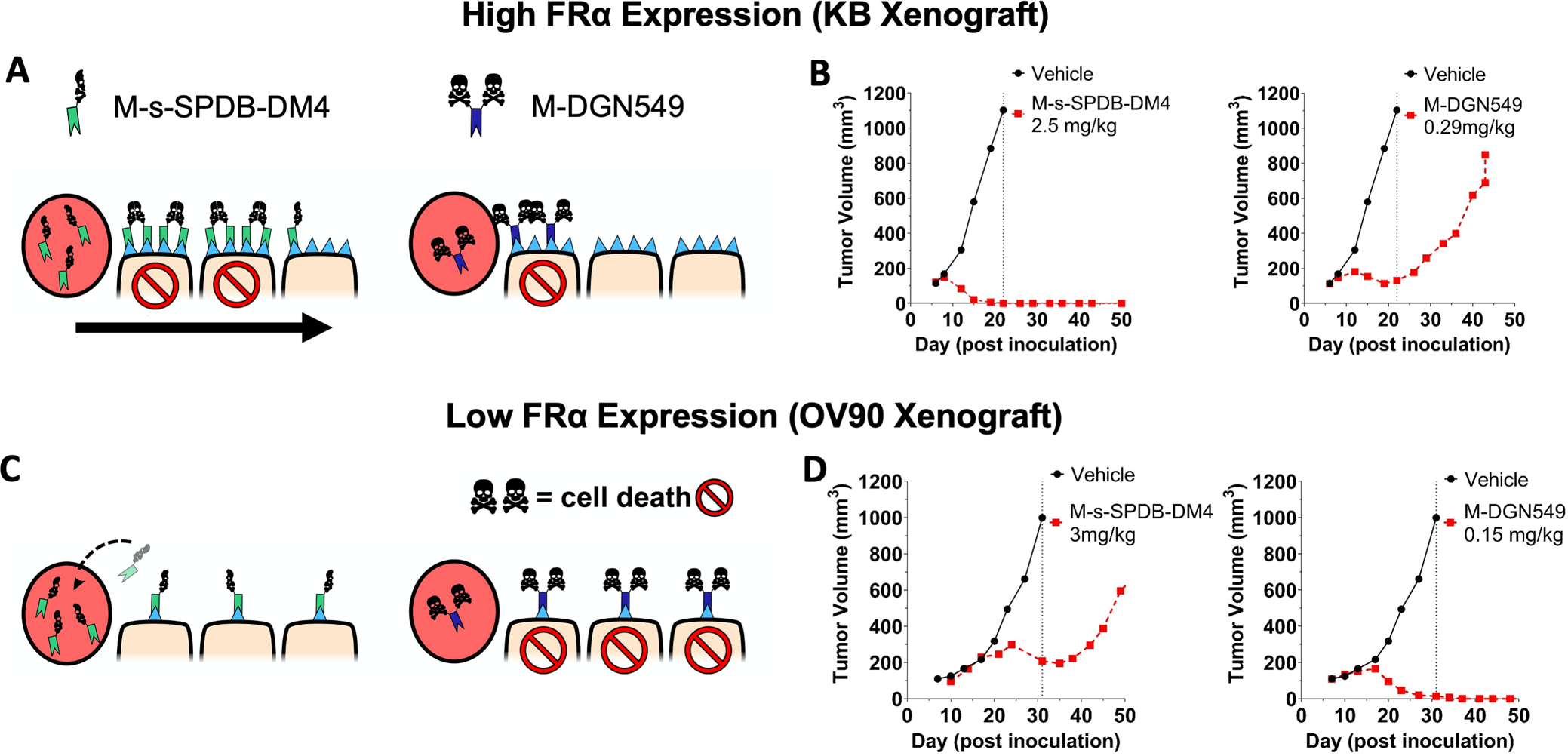
The schematic of half versus two skull and crossbones represents payload potency, not DAR. The high dose of potent DM4 payload in a high FRα expression (KB) tumor model can target more cells with lethal payload concentration (A, left) compared to a lower dose of highly potent DGN549 ADC (A, right). This causes complete tumor regression at clinically tolerable doses of DM4 (B, left) but only a partial response with DGN549, which is tolerated at lower total antibody doses (B, right). This is due to the lower tissue penetration from a reduced antibody dose In a low expression xenograft model (OV90), the FRα-targeting DM4 ADC saturates the tumor (C, left) but can only deliver enough DM4 payload per cell to invoke a partial response (D, left). At super-saturating antibody doses, a significant amount of the ADC washes out of the tumor without being taken up by cells. In contrast, the highly potent DGN549-ADC can penetrate deeper into the tumor tissue while maintaining a lethal dose to the targeted cells (C, right), there by efficiently kill cells with low expression at clinically tolerable doses (D, right). Animals dosed 7 days post inoculation; ADC doses were based on the payload dose (μg payload per kg body weight) but are reported as mg ADC per kg body weight.
