Fig. 2. Molecular validation of zebrafish intracranial lymphatics.
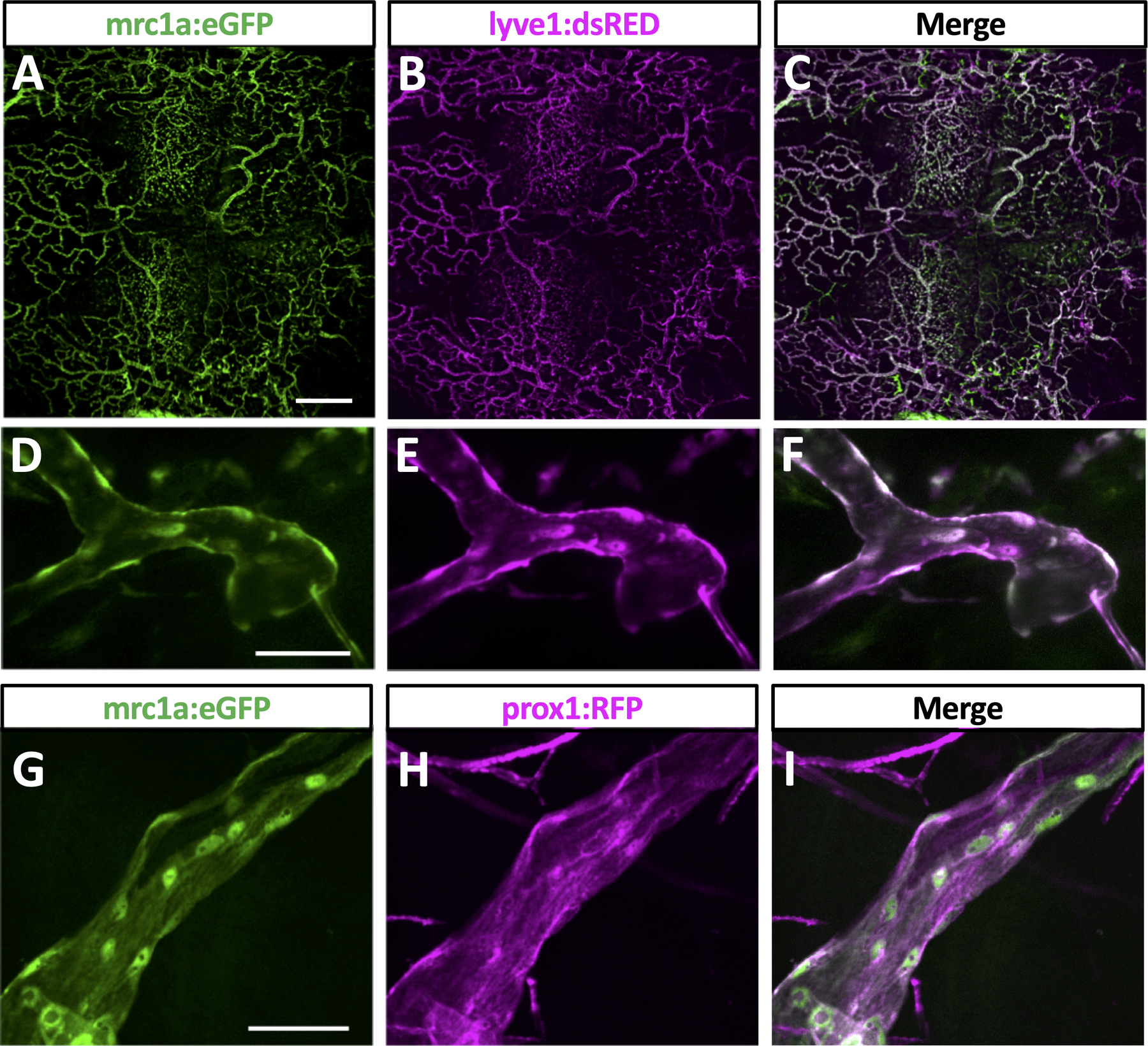
A-C. Confocal imaging overview intracranial and extracranial lymphatic vessel in the dorsal head of an adult casper, Tg(mrc1a:egfp)y251, Tg(−5.2lyve1b:DsRed)nz101 double transgenic zebrafish, showing mrc1a:egfp (A), lyve1b:dsred (B), and combined mrc1a:egfp and lyve1b:dsred (C) images. D-F. Confocal imaging of an intracranial lymphatic vessel in the dorsal head of an adult casper, Tg(mrc1a:egfp)y251, Tg(−5.2lyve1b:DsRed)nz101 double transgenic zebrafish, showing mrc1a:egfp (D), lyve1b:dsred (E), and combined mrc1a:egfp and lyve1b:dsred (F) images. D-F. Confocal imaging of an intracranial lymphatic vessel in the dorsal head of an adult casper, Tg(mrc1a:egfp)y251, Tg(prox1aBAC:KalTA4–4xUAS-E1b:uncTagRFP)nim5 double transgenic zebrafish, showing mrc1a:egfp (D), prox1:rfp (E), and combined mrc1a:egfp and prox1:rfp (F) images. Scale bars: 500 um (A), 50 um (D,G). (Tg-transgenic, mrc1a- mannose receptor C, type 1a, egfp-green fluorescent protein, lyve1b- lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronic receptor 1b, prox1- prospero homeobox 1a)
