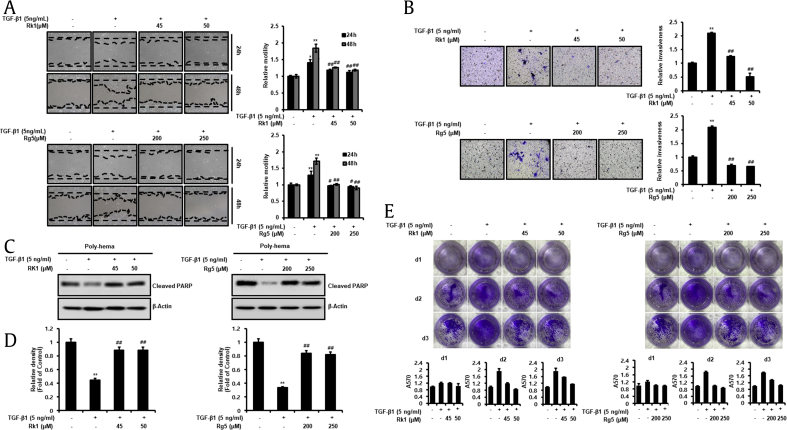
Fig. 5.
Effect of Rk1 and Rg5 on A549 cell migration, invasion and anoikis resistance during inhibition of TGF-β1-induced EMT. A. Rk1 and Rg5 antagonized the TGF-β1-induced migration of A549 cells. When cell confluence had reached about 90%, the cells were scratched with a 200 μL-pipette tip and washed with culture media to remove any free-floating cells and debris. Then culture media was added, and the culture plates were incubated with TGF-β1or with TGF-β1 and Rk1 or Rg5. The cells were photographed under a microscope 48 h after scratching. Relative motility was quantified by measuring the cell surface area with Image J program. B. Rk1 and Rg5 inhibited TGF-β1-induced invasion. Effect of Rk1 and Rg5 on A549 cell invasion in a 200 × light scope after staining by Matrigel invasion assay as described in Section 2.10. In vitro invasiveness of A549 cells were measured by counting cells that migrated through the extracellular matrix layer of invasion chambers. C and D. Rk1 and Rg5 suppressed TGF-β1-induced anoikis resistance. A549 cells were pretreated with the indicated concentration of Rk1 or Rg5 for 2 h and then stimulated with TGF-β1 (5 ng/mL) for 48 h. The cells were then cultured on poly(hydroxyethyl methacrylate) [poly-HEMA]-coated plates for 48 h at TGF-β1 (5 ng/mL) with or without Rk1 or Rg5 condition. The cells were harvested and then lysed. Cleaved pPARP)-1, apoptosis marker, was detected by Western blotting. Densitometric analysis of band intensity of cleaved PARP-1was performed. E. Rk1and Rg5 lead to increased cell survival of suspended cells. A549 cells (1 × 106) were grown in suspension for 0 to 3 d in treated with TGF-β1 and/or Rk1 or Rg5, and subsequently transferred into six-well adhesive plates followed by Coomassie staining. Columns mean of three separate experiments; bars. ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗p < 0.05 vs control and ##p < 0.01 #p < 0.05 versus TGF-β1 treated control. The data are expressed as mean ± SD for triplicates.