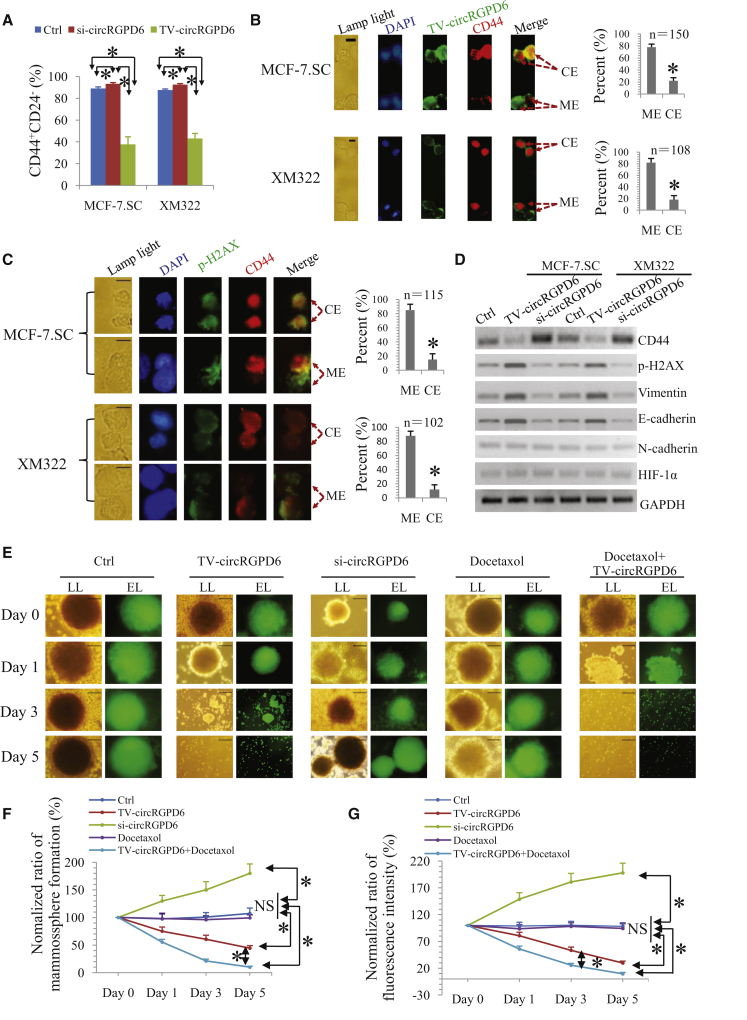
Figure 4.
TV-circRGPD6 Inhibits Tumor-Initiating Properties of BCSCs In Vitro
(A) Flow cytometry analysis of CD44+CD24− expressions in MCF-7.SC and XM322 after transfection of either si-circRGPD6 or TV-circRGPD6. (B) Representative microscope images of coimmunofluorescence (left panel) as well as statistical results (right panel) of TV-circRGPD6-GFP and CD44-phycoerythrin (PE) are either mutually exclusive (ME) or coexpressed (CE) in at least one of the daughter cells during BCSC divisions. Scale bars, 10 μm. (C) Representative microscope images of coimmunofluorescence (left panel) as well as statistical results (right panel) of p-H2AX and CD44 expression in daughter cells of BCSCs during division after transfection of TV-circRGPD6 in clonal pair-cell assays. Scale bars, 10 μm. (D) Western blots for CD44, p-H2AX, vimentin, E-cadherin, N-cadherin, HIF-1α, and GAPDH expression in MCF-7.SC and XM322, with or without transfection of TV-circRGPD6 and si-circRGPD6. (E) TV-circRGPD6 synergizes with docetaxel to eradicate XM322. Representative bright field or fluorescence images of XM322 in mammosphere-formation assay. XM322, which is GFP labeled, was treated with TV-circRGPD6, si-circRGPD6, docetaxel, and TV-circRGPD6 plus docetaxel, respectively. Bright field (lamp light [LL]; left panel) or laser with excitation wavelength (EL; right panel) was used to detect the depression effects. Scale bars, 100 μm. (F and G) Quantification of (F) mammosphere formation and (G) fluorescence expressions of XM322 after treatments of Ctrl, TV-circRGPD6, si-circRGPD6, docetaxel, and docetaxel combined with TV-circRGPD6. Mammospheres larger than or equal to 50 μm in diameter were counted. Statistical analyses were performed using the paired t test. Each experiment was repeated at least three times. ∗p < 0.05; NS, not significant.