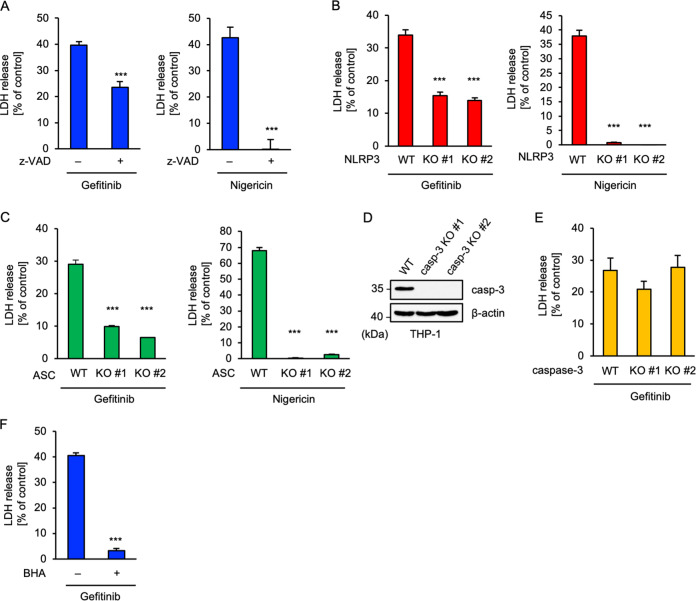
Fig. 4. Gefitinib-driven mtROS cause pyroptosis.
A The inhibitory effect of z-VAD on gefitinib-induced cell death. PMA-differentiated THP-1 cells were pretreated with 20 μM z-VAD for 0.5 h and then treated with 20 μM gefitinib for 8 h or 5 μM nigericin for 2 h. Cell cytotoxicity was measured by LDH release assay. Data shown are the mean ± S.D. Significant differences were determined by student’s t-test; ***p < 0.001. B, C Requirement of NLRP3 or ASC for gefitinib-induced cell death. PMA-differentiated WT and NLRP3 KO (B) or ASC KO (C) THP-1 cells were treated with 20 μM gefitinib for 8 h or 5 μM nigericin for 2 h. Cell cytotoxicity was measured by LDH release assay. Data shown are the mean ± S.D. Significant differences were determined by student’s t-test; ***p < 0.001. D Immunoblot analysis of caspase-3 in THP-1 cells. Whole-cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. E Requirement of caspase-3 for gefitinib-induced cell death. PMA-differentiated WT and caspase-3 KO THP-1 cells were treated with 20 μM gefitinib for 8 h. Cell cytotoxicity was measured by LDH release assay and cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Data shown are the mean ± S.D. F The inhibitory effect of BHA on gefitinib-induced cell death. PMA-differentiated THP-1 cells were pretreated with 100 μM BHA for 0.5 h and then treated with 20 μM gefitinib for 8 h. Cell cytotoxicity was measured by LDH release assay. Data shown are the mean ± S.D. Significant differences were determined by student’s t-test; ***p < 0.001. All data in Fig. 4 are representatives of at least five independent experiments.