FIGURE 5.
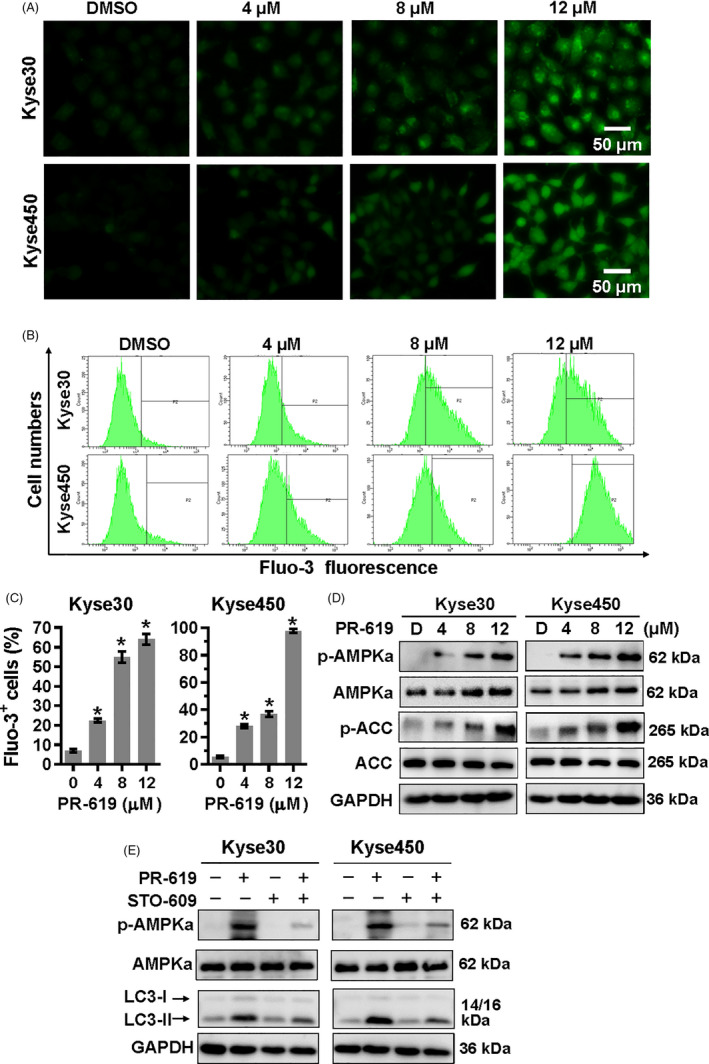
Ca2+‐CaMKKβ signalling in PR‐619 treatment cells was involved in AMPKα activation. A to C, Detection of intracellular Ca2+. Kyse30 and Kyse450 cells were treated with PR‐619 as indicated. Twenty‐four h later, cells were collected and washed with PBS. Then, Fluo‐3AM was added into the cells as described in the instruction and incubated for 30 min at 37℃. Cells were washed with PBS again and pictures were captured under a microscope. Represented pictures were shown in panel A. Fluo‐3+ cells were detected (B) and statistically analysed (C) using FACS. D, PR‐619 treatment activated AMPKα. Kyse30 and Kyse450 cells were treated with PR‐619, as indicated. Cells were collected, and proteins were extracted and analysed by Western blotting with specific antibodies. GAPDH was used as the loading control. E, STO‐609 inhibited the activation of AMPKα and rescued autophagy in PR‐619‐treated cells. Kyse30 and Kyse450 cells were treated with PR‐619 single (8 µmol/L) or combined with STO‐609 (10 µmol/L). Then, proteins were extracted and analysed using specific antibodies against AMPKα, p‐AMPKα and LC3. GAPDH was used as the loading control. All data were representative of at least three independent experiments (n = 3; error bar, SD)
