FIGURE 6.
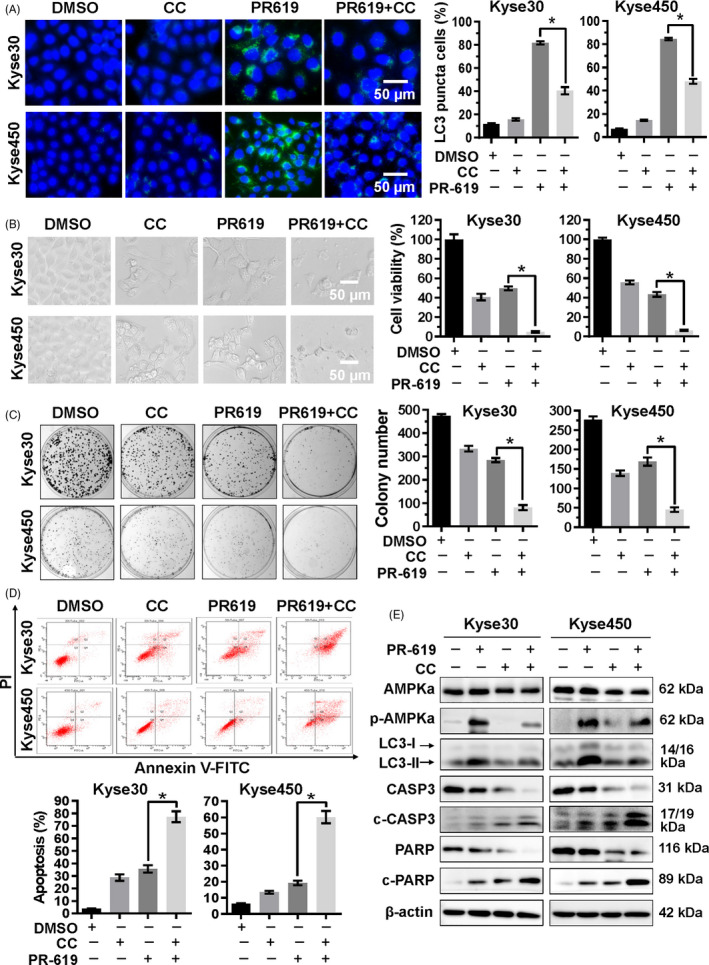
AMPK signalling pathway was involved in the PR‐619‐induced autophagy and apoptosis. A, Blockage of AMPK reduced PR‐619 induced autophagy. Kyse30 and Kyse450 cells were treated with PR‐619 single (8 µmol/L) or combined with CC (8 µmol/L), an AMPK inhibitor. LC3 was detected using immunofluorescence assay as described in material and methods, reprehensive pictures were captured (left panel), and LC3 puncta cells were statistically analysed (right panel). B, Blockage of AMPK enhanced the inhibition of cell viability in PR‐619‐treated cells. Kyse30 and Kyse450 cells were treated with PR‐619 single (8 µmol/L) or combined with CC (4 µmol/L) as described above. Cell proliferation was observed and captured under inverted microscope (left panel). Cell viability was detected using CCK‐8 assay (right panel). C, Blockage of AMPK inhibited colony formation. Kyse30 and Kyse450 cells were treated with PR‐619 single (3 µmol/L) or combined with CC (2 µmol/L) for 10 days and then fixed, stained captured (left panel) and counted (right panel). D, Blockage of AMPK accelerated PR‐619 triggered apoptosis. Kyse30 and Kyse450 cells were treated with PR‐619 single (8 µmol/L) or combined with CC (8 µmol/L). Apoptosis was determined by FACS analysis using Annexin V‐FITC/PI double‐staining kit (left panel), and Annexin V+ cell populations were defined as apoptosis (right panel). E, Effect of CC and PR‐619 co‐treatment on protein expression. Kyse30 and Kyse450 cells were treated with PR‐619 single (8 µmol/L) or combined with CC (8 µmol/L). Then, proteins were extracted and analysed by Western blotting with specific antibodies. GAPDH was used as the loading control. All data were representative of at least three independent experiments (n = 3; error bar, SD)
