Figure 1.
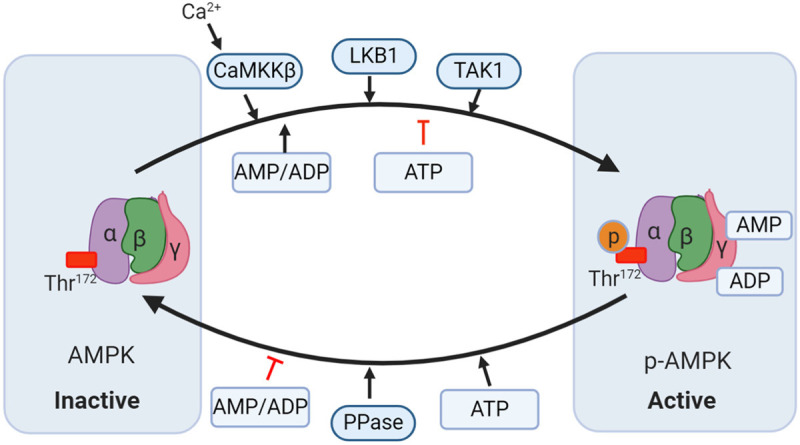
Mechanisms modulating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activity. AMPK consists of α, β, and γ subunits. There are two distinct ways to trigger AMPK activation. i): AMP and ADP bind to the γ subunits and allosterically activate AMPK; ii) Phosphorylation of Thr172 in the α subunit by upstream kinases such as liver kinase B1 (LKB1), calcium-calmodulin-dependent kinase 2 (CaMKK2), and transforming growth factor-β-activated protein kinase-1 (TAK1) induces the activation of AMPK. AMPK is dephosphorylated by protein phosphatase (PP) thereby being inhibited. Moreover, ATP can also oppose the activation of AMPK by inhibiting the γ subunits that are dependent on allosteric activation and phosphorylating the LKB1-induced α subunit.
