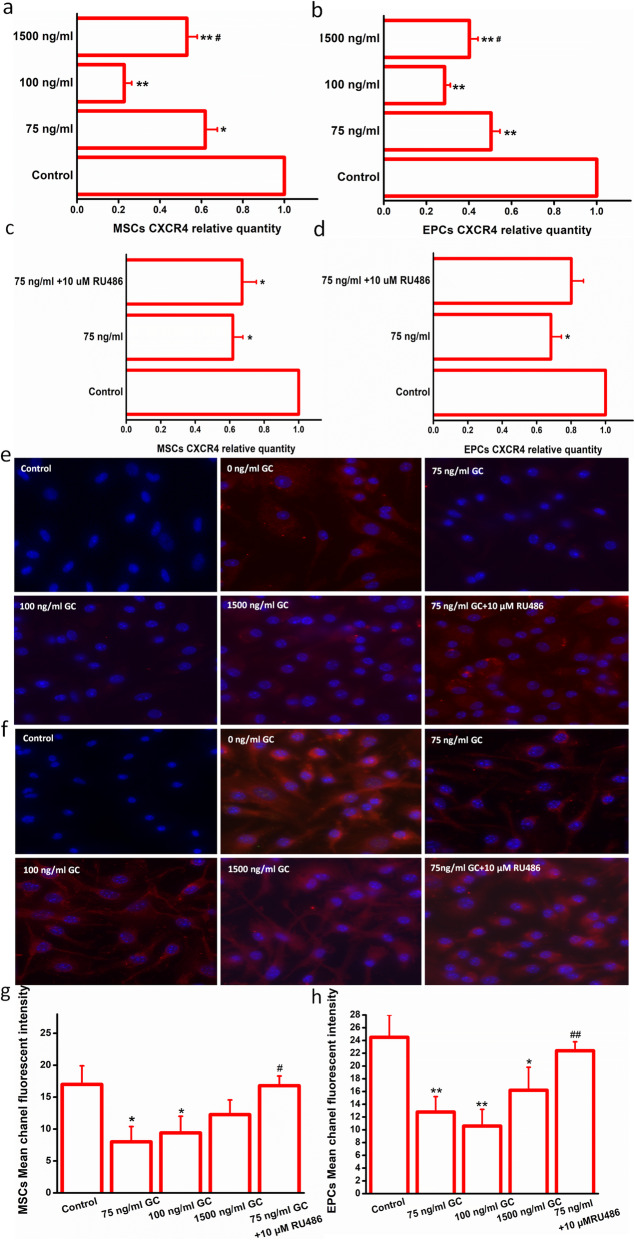
Fig. 3.
Glucocorticoid inhibited the CXCR4 expression of bone marrow-derived stem/progenitor cell subsets via FPR. a GC inhibited the CXCR4 mRNA expression in MSCs. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. the control group. #P < 0.05 vs. the 75 ng/ml group. b GC inhibited the CXCR4 mRNA expression in EPCs. **P < 0.01 vs. the control group. #P < 0.05 vs. the 75 ng/ml and 100 ng/ml groups. c RU486 reversed the GC-induced CXCR4 mRNA expression in MSCs. *P < 0.05 vs. the control group. d RU486 reversed the GC-induced CXCR4 mRNA expression in EPCs. *P < 0.05 vs. the control group. e, g CXCR4 protein expression in MSCs. *P < 0.05 vs. the 0 ng/ml group. Control: the negative control. f, h CXCR4 protein expression in EPCs. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. the 0 ng/ml group. Control: the negative control. ##P < 0.01 vs. the 75 ng/ml group. MSCs, mesenchymal stem cells; EPCs, endothelial progenitor cells; GC, glucocorticoid; FPR, formyl peptide receptor. Data are mean ± SD of six representative observations