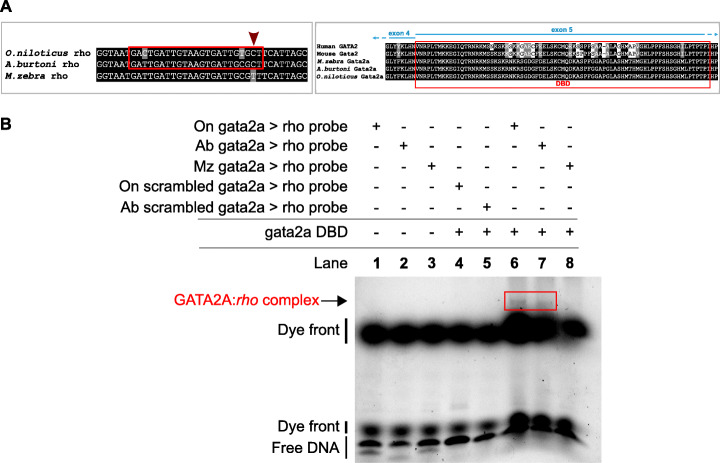
Fig. 4.
Evolution of the rhodopsin regulatory networks in O. niloticus, A. burtoni and M. zebra. a On the left, GATA2A motif prediction in reverse orientated O. niloticus and A. burtoni rhodopsin gene promoter (red box) and substitution demarcated in M. zebra rhodopsin gene promoter (red arrow). On the right, GATA2A partial protein alignment showing DNA-binding domain (DBD) annotation in human, mouse, O. niloticus, A. burtoni and M. zebra. b EMSA validation of GATA2A DBD binding to O. niloticus and A. burtoni rhodopsin gene promoter. Table denotes combinations of DNA probe and expressed DBD in EMSA reactions that include negative controls (lanes 1 to 5); O. niloticus (lane 6), A. burtoni (lane 7) and M. zebra (lane 8) protein: DNA-binding assays. GATA2A:rho complex formed in O. niloticus (lane 6) and A. burtoni (lane 7) as confirmed by band shift (red box) and no complex formed in M. zebra (lane 8)