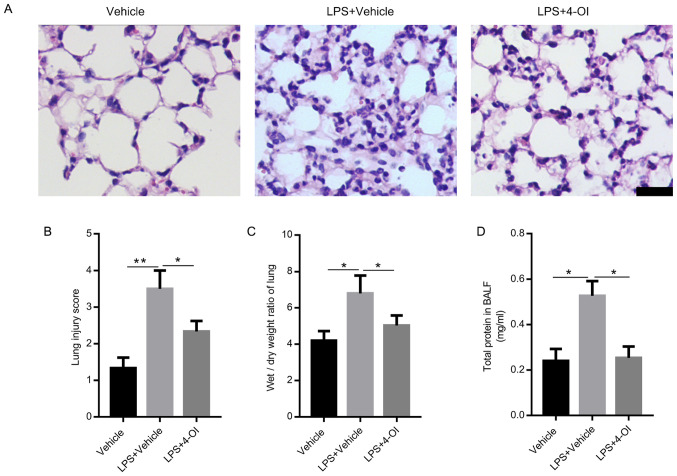
Figure 1.
4-OI alleviates lung injury induced by LPS in mice. Treatment of mice with 4-OI at doses of 25 mg/kg was administered intraperitoneally, and the control group received an equivalent volume of vehicle [(2-hydroxypropyl)-β-cyclodextrin in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)] 2 h before saline or LPS injection (5 mg/kg, intratracheal). Twelve hours later, the mice were sacrificed. Hematoxylin and eosin staining (A, bar=100 µm) was used to detect the lung histopathological changes. (B) Lung injury scores were determined using four independent parameters, namely alveolar congestion, hemorrhage, leukocyte infiltration and alveolar wall thickness. The lung wet/dry ratio (C) and total protein in BALF (D) were measured to determine lung permeability (n=5). Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01. 4-OI, 4-octyl itaconate; LPS, lipopolysaccharides; BALF, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid.