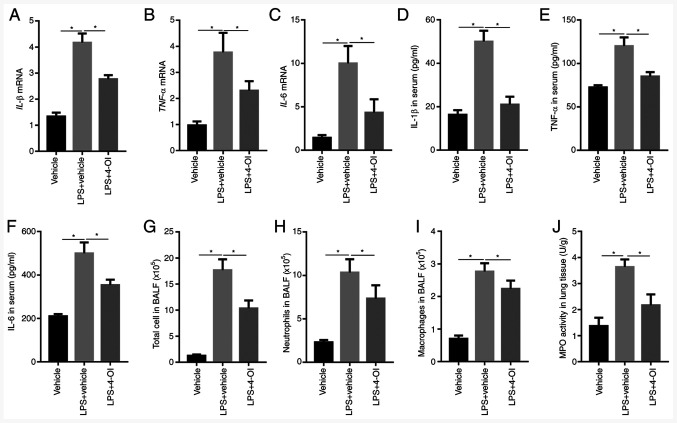
Figure 2.
4-OI inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory responses in mice with acute lung injury. Treatment of mice with 4-OI at doses of 25 mg/kg was administered intraperitoneally, and the control group received an equivalent volume of vehicle [(2-hydroxypropyl)-β-cyclodextrin in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)] 2 h before saline or LPS injection (5 mg/kg, intratracheal). Twelve hours later, IL-1β (A), TNF-α (B), and IL-6 (C) mRNA levels in the lungs were determined by reverse transcription-quantitative PCR (n=5). IL-1β (D), TNF-α (E), and IL-6 (F) protein contents in serum were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (n=5). Twelve hours later, total cells (G), neutrophils (H) and macrophages (I) in BALF were assessed (n=5). MPO activity (J) in lung tissue was determined (n=5). Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. *P<0.05. 4-OI, 4-octyl itaconate; LPS, lipopolysaccharides; IL, interleukin; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; BALF, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid; MPO, myeloperoxidase.