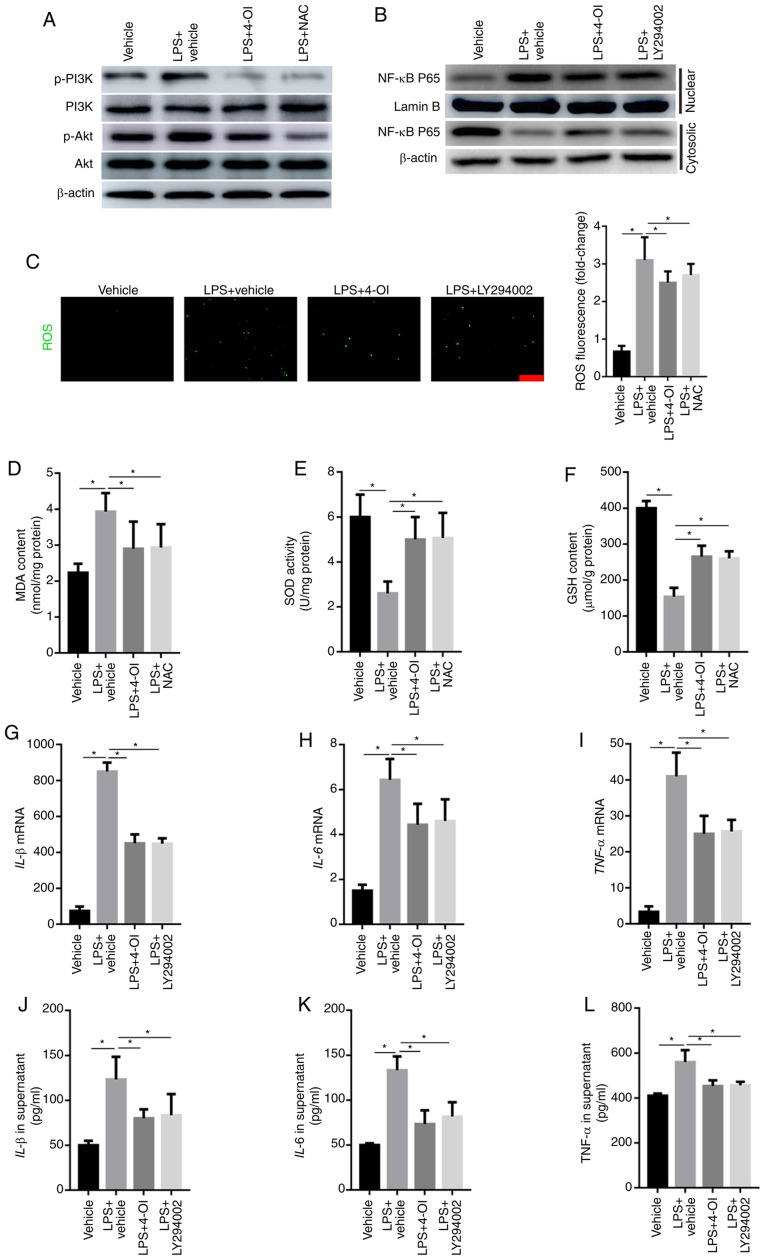
Figure 4.
4-OI decreased the induction of inflammatory cytokines by inhibiting ROS-mediated PI3K/Akt/NF-κB activation in LPS-treated macrophages. RAW264.7 macrophage cells were pretreated with 4-OI (125 µM), NAC (10 mM), the PI3K inhibitor LY294002 (25 µM) or vehicle control for 1 h and then stimulated with LPS (1 µg/ml) for 30 min to detect the phosphorylated levels of PI3K and Akt and the expression of NF-κB p65 in the nuclear and cytosolic fractions in LPS-treated macrophages and for 24 h to quantify ROS production, MDA content, SOD activity and GSH content and the concentration of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 in macrophages. The phosphorylated levels of PI3K and Akt (A) and the expression of NF-κB p65 in the nuclear and cytosolic fractions (B) of LPS-treated macrophages were detected by western blotting. ROS generation (bar=100 µm) (C), MDA content (D), SOD activity (E) and GSH content (F) in RAW264.7 macrophage cells were determined. The expression of IL-1β (G), IL-6 (H) and TNF-α (I) in macrophages was measured by qPCR. IL-1β (J), IL-6 (K) and TNF-α (L) protein contents in the supernatant of RAW264.7 macrophage cells were determined. Data represent the means ± SEM of three independent experiments. *P<0.05. 4-OI, 4-octyl itaconate; LPS, lipopolysaccharides; NAC, N-acetyl-L-cysteine; ROS, reactive oxygen species; MDA, malondialdehyde; SOD, superoxide dismutase; GSH, glutathione; IL, interleukin; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.