Fig. 2.
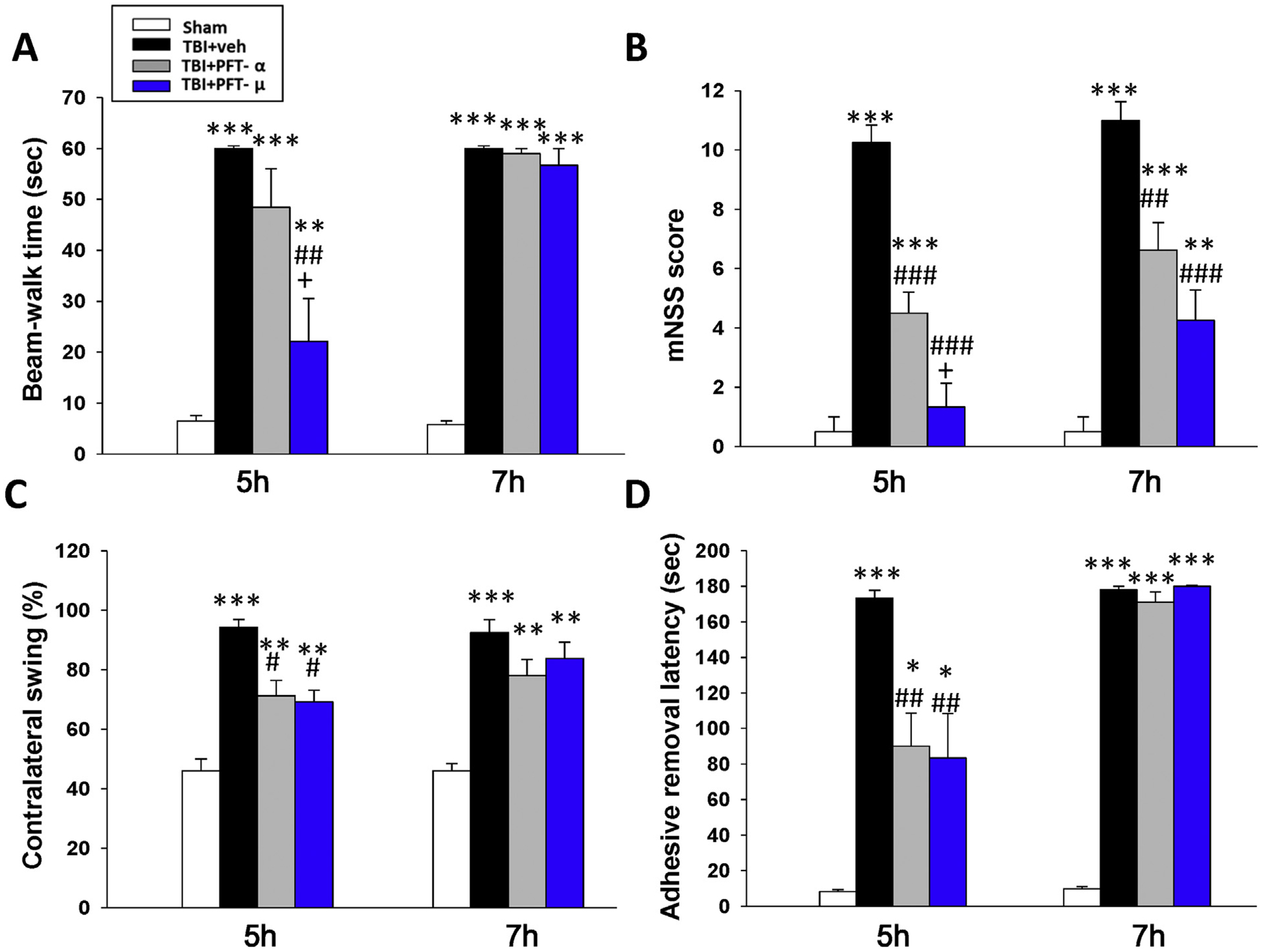
Post-injury administration of PFT-α or PFT-μ given at 5 h improved functional outcomes, as revealed by multiple behavioral evaluations undertaken at 24 h post CCI or sham challenge. (A) Motor coordination measured by beam walking test. (B) Neurological function measured by mNSS. (C) Motor asymmetry measured by elevated body swing test (EBST). (D) Sensory-motor function measured by tactile adhesive removal test. Data represent the means ± SEM. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001 versus sham group; #P < .05, ##P < .01, ###P < .001 versus TBI + vehicle (veh) group; +P < .05 versus TBI + PFT-α group. (n = 8 in TBI + veh and TBI + PFT-α group, n = 5 in sham and TBI + PFT-μ group). Note that when PFT treatment was administered at 7 h post injury, it proved much less effective.
