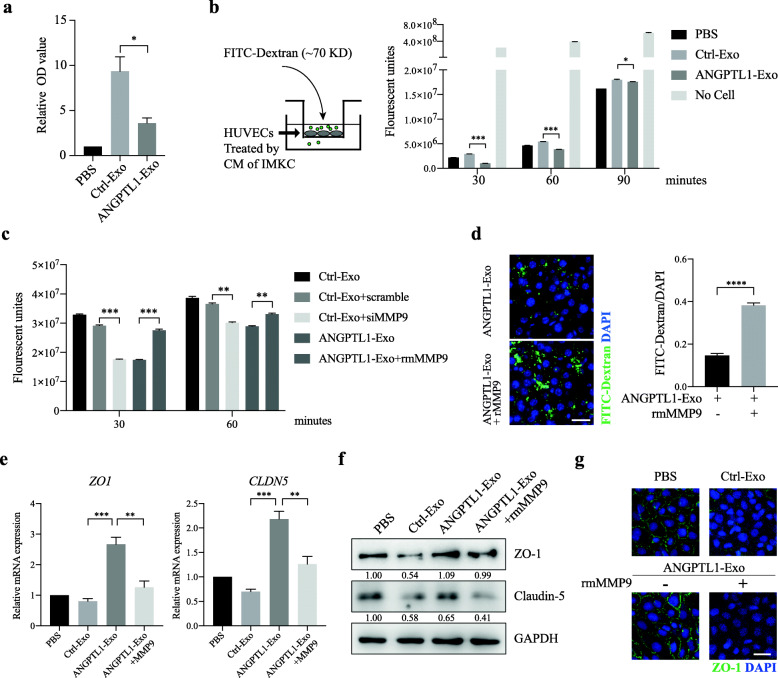
Fig. 4.
Exosomal ANGPTL1 dependent MMP9 decrease normalized vascular leakiness induced by CRC derived exosomes. a ELISA analysis of MMP9 level in the culture medium (CM) from ImKC educated by PBS, Ctrl-Exo or ANGPTL1-Exo for 24 h. b, c Permeability of the HUVEC monolayers to FITC–Dextran (70 kDa) after exposure to CM from ImKC educated by PBS, Ctrl-Exo, ANGPTL1-Exo (b), or exposure to CM from ImKC educated by Ctrl-Exo followed by transfection of control siRNA (scramble) or MMP9 siRNA or by ANGPTL1-Exo with extra rmMMP9 (100 ng/mL) (c). The fluorescence in the bottom well was detected every 30 min. d rmMMP9 (50 μg/kg) was injected through the tail vein into the mice educated by ANGPTL1-Exo for 1 h. In vivo vascular permeability was then determined (n = 3). Representative images are shown (left). Data were presented as FITC-dextran /DAPI ratio (right). e, f ZO-1 and Claudin-5 expression in HUVECs treated by ImKC CM were detected through qRT-PCR (e) and WB (f). g Immunofluorescence staining of ZO-1 in HUVECs monolayers treated by ImKC CM. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Data in panel a, d and e were analyzed using t-test, in panel b and c were analyzed using ANOVA. The scale bar represents 20 um. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001