Figure 2. Oxidized LDL stimulates macrophage microparticle production.
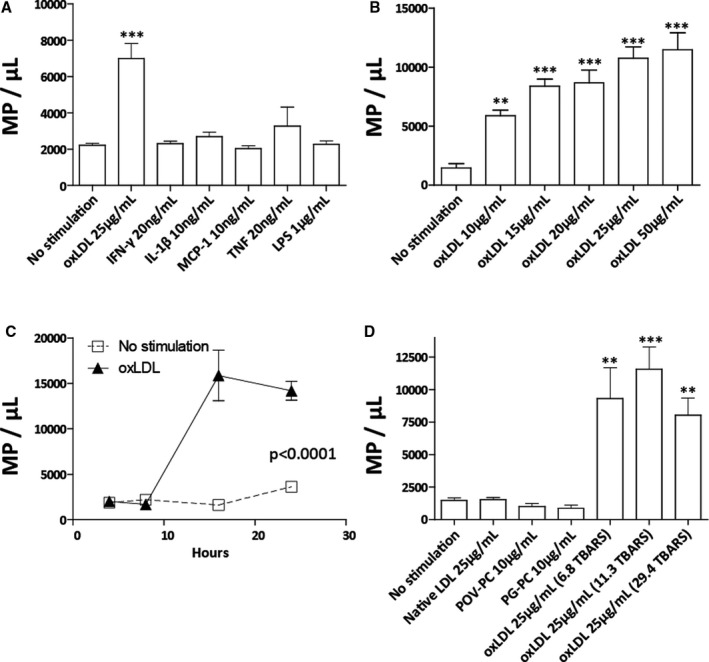
Macrophage stimulation with atherogenic cytokines and oxLDL. OxLDL treatment (30.3 TBARS, 16 hours) led to a 416% increase in macrophage microparticle (MΦMP) production (A). OxLDL‐induced MΦMP production in relation to oxLDL concentration (30.3 TBARS, 16 hours) (B), and hours of stimulation (25 µg/mL, 29.4 TBARS) (C). MΦMP production in response to stimulation with nonoxidized LDL, minimally modified oxLDL components POV‐PC and PG‐PC, or oxLDL with 6.8, 11.3, and 29.4 TBARS oxidation (D). (TBARS in nmol/L of malondialdehyde/mg of LDL protein) (*P<0.05, **P<0.01, and ***P<0.001 vs. no stimulation). IFN‐γ indicates inteferon–γ; Il‐1β, interleukin‐1β; LDL, low‐density lipoprotein; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; MCP‐1, monocyte chemotactic protein 1; oxLDL, oxidized low‐density lipoprotein; PG‐PC, 1‐palmitoyl‐2‐glutaryl phosphatidylcholine; POV‐PC, 2‐(5‐oxovalery) phosphatidylcholine; TBARS, thiobarbituric acid reactive substances; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
