Figure 6. Gremlin‐1 expression increased in patients with congenital heart disease with Eisenmenger syndrome (CHD‐ES).
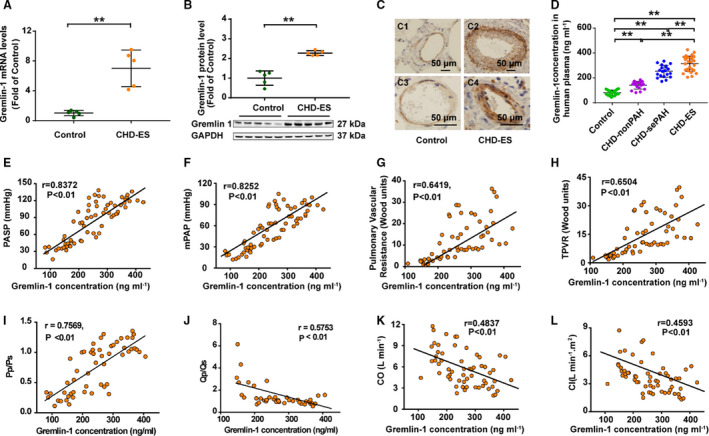
A, mRNA level of gremlin‐1 in patients with CHD‐ES (n=5) and control subjects (n=5). B, Representative Western blotting image of gremlin‐1 protein level (lower panel) and densitometric analysis (upper histogram) in patients with CHD‐ES (n=5) and control subjects (n=5). C, Representative images of immunohistological staining of gremlin‐1 in control lungs (C1 and C2, ×40) and lungs with CHD‐ES (C3 and C4, ×100) (bar=50 μm). D, Plasma level of gremlin‐1 demonstrated a stepwise increase with the extent of CHD‐associated pulmonary arterial hypertension (CHD‐PAH). E through L, Plasma level of gremlin‐1 positively correlated with pulmonary arterial systolic pressure (PASP) (E), mean pulmonary arterial pressure (mPAP) (F), pulmonary vascular resistance (G), total pulmonary vascular resistance (TPVR) (H), and ratio of pulmonary arterial systolic pressure/systemic arterial systolic pressure (Pp/Ps) (I), and negatively correlated with pulmonary/systemic shunt volume ratio (Qp/Qs) (J), cardiac output (CO) (K), and cardiac index (CI) (L). sePAH indicates severe PAH. **P<0.01.
