Figure 5. Chemical modifications of collagen induced by various fixatives.
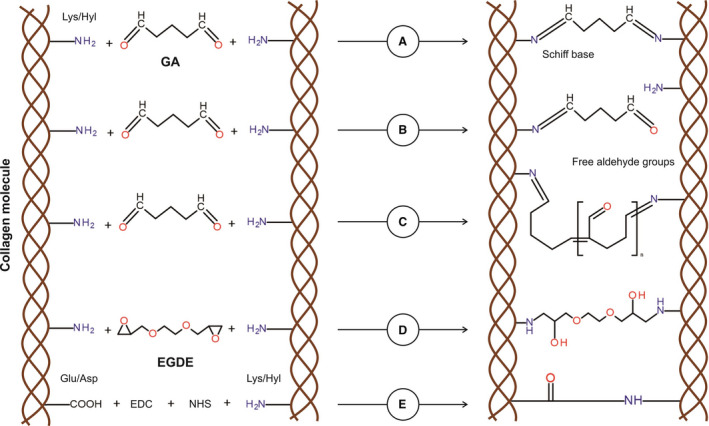
A, Aldehyde groups of glutaraldehyde (GA) interact with amino group of lysine (Lys) or hydroxylysine (Hyl) residues within the collagen, thereby forming a stable chemical bond (Schiff base) for a stable cross‐linking. B, One of GA aldehyde groups interacts with a collagen amino group, resulting in a cross‐linking, whereas the second aldehyde group remains free to other chemical interactions, including calcium binding. C, Polymerization of GA is performed through aldol condensation. Despite collagen molecules that are cross‐linked, free aldehyde groups still remain. D, All epoxy groups of ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether (EGDE) interact with amino group of Lys or Hyl residues within the collagen, forming a stable covalent bond for a stable cross‐linking. E, Collagen fixation with 1‐ethyl‐3‐(3‐dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide (EDC) and N‐hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) is conducted via the activation of carboxyl groups of aspartic acid/glutamic acid residues in the peptide chain and through the formation of intermediate compound, which is able to interact with free amino groups of lysine or hydroxylysine.
