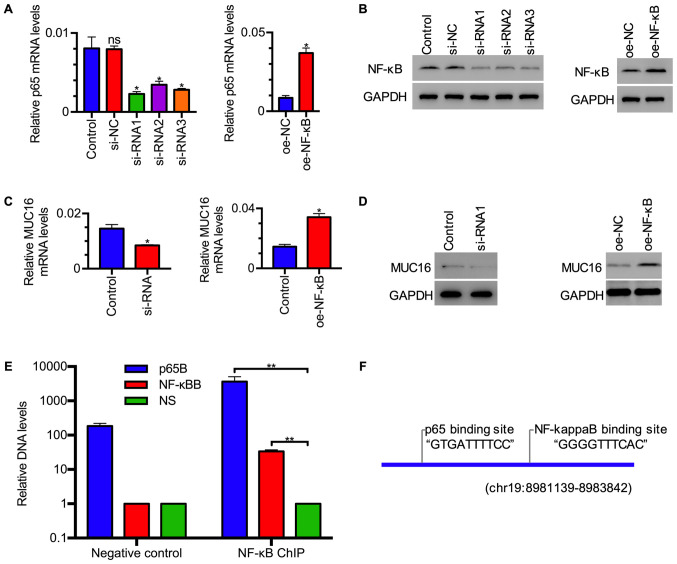
Figure 5.
NF-κB/p65 enhances MUC16 expression by binding to its gene promoter. (A) NF-κB mRNA expression levels relative to GAPDH in HEY cells following NF-κB knockdown and overexpression (n=3). Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. *P<0.05 vs. control or oe-NC. (B) NF-κB protein expression levels in HEY cells following NF-κB knockdown and overexpression. (C) MUC16 mRNA expression levels relative to GAPDH in control, NF-κB knockdown and NF-κB overexpression HEY cells (n=3). *P<0.05 vs. control. (D) MUC16 protein expression levels in control, NF-κB knockdown and NF-κB overexpression HEY cells. (E) Quantitative analysis of relative DNA levels collected after chromatin immunoprecipitation (n=3). Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. **P<0.01. (F) Potential NF-κB/p65 binding sites on the MUC16 promoter. NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; si, small interfering RNA; oe, overexpression; NC, negative control; MUC16, mucin 16 cell surface associated.