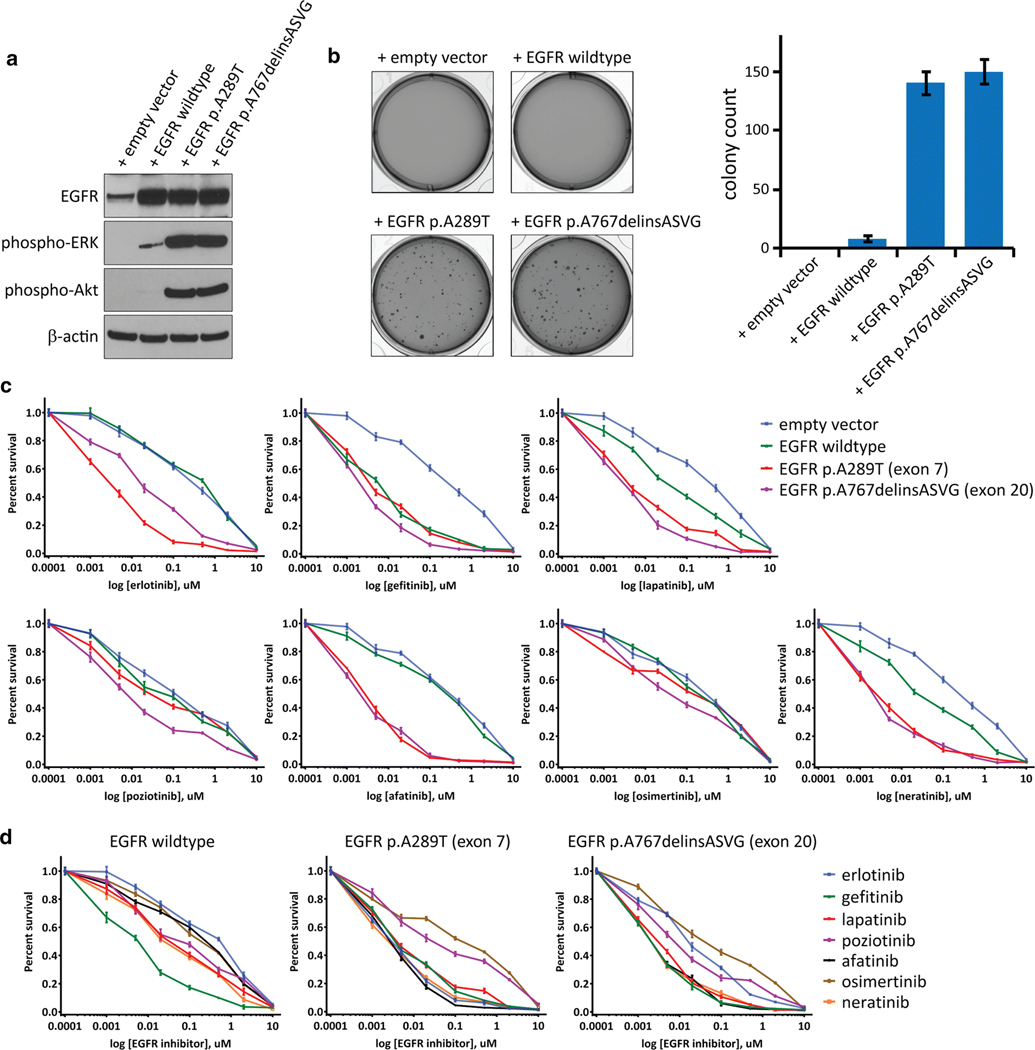
Fig. 4.
EGFR mutations in pediatric bithalamic gliomas are oncogenic and confer sensitivity to specific tyrosine kinase inhibitors. a, Western blots on total cell lysate from SVG-p12 immortalized human astrocytes after lentiviral transduction with empty vector, EGFR wildtype, or EGFR mutant isoforms. b, Colony formation in soft agar of SVG-p12 immortalized human astrocytes after lentiviral transduction with empty vector, EGFR wildtype, or EGFR mutant isoforms. Images of representative wells (left) and quantitation of colony number per well (right) are shown. Error bars represent standard error from the mean of twelve replicates from two independent experiments. c, Survival plots of SVG-p12 immortalized human astrocytes transduced with empty vector, EGFR wildtype, and EGFR mutant isoforms followed by treatment with various tyrosine kinase inhibitors at the indicated doses for 72 hours. Each data point is the mean of 9 replicates from three independent experiments, and error bars show standard error of the mean. d, Comparison of kinase inhibitor efficacy in SVG-p12 immortalized human astrocytes expressing EGFR wildtype or mutant isoforms.