Figure 4.
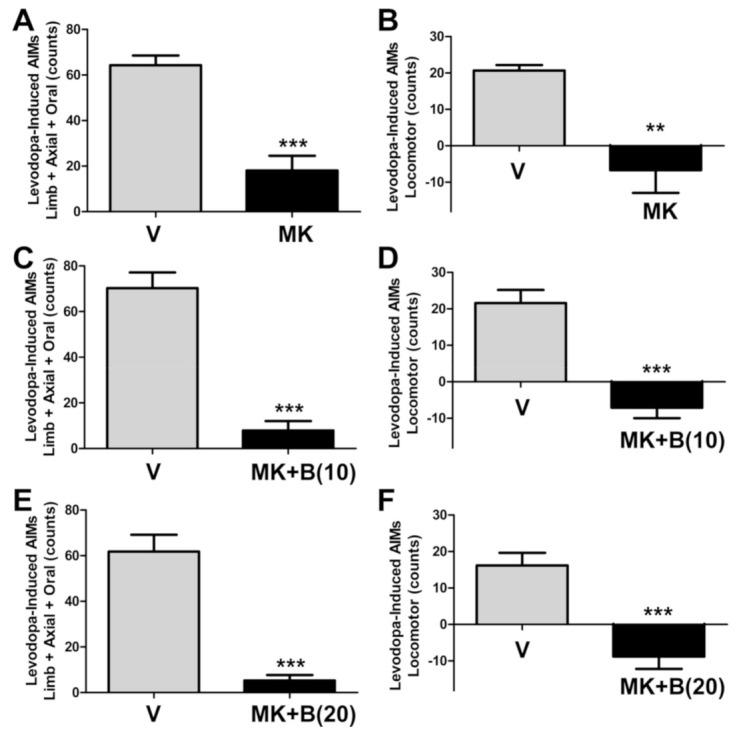
The DOR-specific opioid glycopeptide BBI-11008 did affect neither the anti-dyskinetic nor the pro-Parkinsonian activity of MK-801. (A) MK-801 (0.3 mg/kg) efficiently blocked LAO AIMs. Co-injection of 10 mg/kg (C) and 20 mg/kg (E) BBI-11008 (i.p.) did not change the effect of MK-801 to reduce LAO AIMs (p = 0.24, Kruskal-Wallis test of MK vs. MK+B(10) and MK+B(20) groups in A, C and E). (B) MK-801 (0.3 mg/kg) caused ipsiversive turns, a surrogate measure for pro-Parkinsonian activity in this model. Neither 10 mg/kg (D) nor 20 mg/kg (F) BBI-11008 abolished MK-801-induced ipsiversive locomotor AIMs (p = 0.8, Kruskal–Wallis test of MK vs. MK+B(10) and MK+B(20) groups in B, D and F). Data in all graphs are presented as mean AIMs count ± SEM, *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, n = 5, paired Wilcoxon signed-rank tests vs. corresponding vehicle control.
