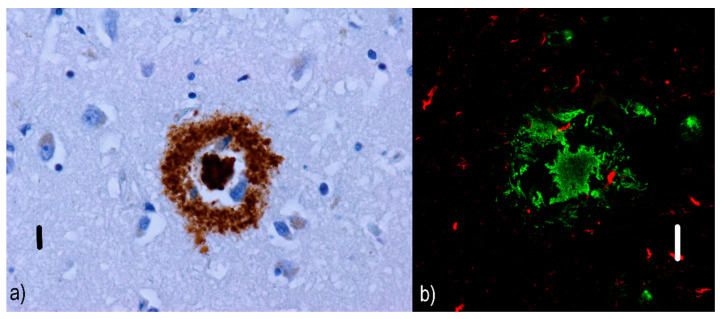
Figure 3.
Cored neuritic plaques: (a) immunofluorescence visualization of cored Aβ plaque in an AD patient. The dense Aβ core is encircled by fibrillar Aβ deposits, which are clearly visible in cored neuritic plaques. Primary antibodies: anti-beta amyloid rabbit IgG. The original magnification was 400×. The scale bar indicates a length of 10 micrometers. (b) Simultaneous imaging with a confocal fluorescent laser scanning microscope shows the presence of an Aβ core with fibrillar Aβ structures (green) in the vicinity as well as a few tau-positive dystrophic neurites (red). Primary antibodies: Anti-beta amyloid rabbit IgG and AT8 (murine anti-hyperphosphorylated protein tau). The secondary antibody was conjugated with either Alexa®488 (anti-rabbit IgG, green) or Alexa®568 (anti-mouse IgG, red). The scale bar indicates a length of 10 micrometers. The images are from a male 67-year-old patient with EOAD and come from the cornu ammonis, but similar findings were present in all areas of the hippocampal formation and adjacent para-hippocampal and entorhinal cortex. Neuropathological diagnosis: Fully developed early-onset form of Alzheimer’s disease in the neocortical stage (Braak VI, CERAD C) with marked amyloid angiopathy (CAA Vonsattel grade 3). According to the revised “ABC” of the NIA classification, the changes associated with AD are at a “high” level (A3B3C3).