Figure 4.
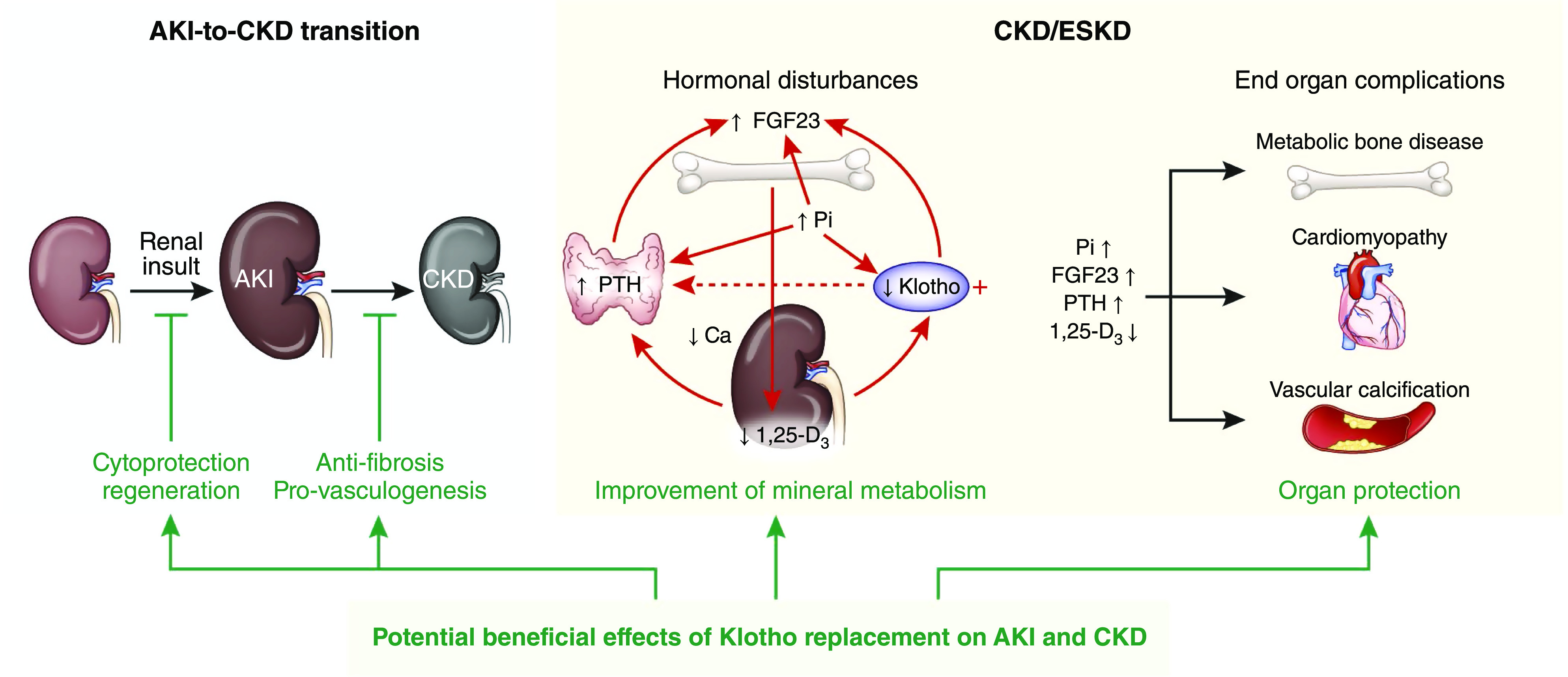
Role of Klotho in kidney and cardiovascular protection. AKI occurs after exposure to kidney insults. If the insult is strong or long enough, kidney recovery is impaired, and AKI progresses to CKD. With CKD progression, kidney Klotho is decreased followed by increase in circulating FGF23 levels, low 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, high blood phosphate, and increase in PTH. Abnormal mineral hormones individually and synergistically exacerbate each other in the manner of a vortex of downhill spiral (dashed line: putative action) and contribute to end organ complications, including CKD-MBD, uremic cardiomyopathy, and vascular calcification. Klotho replacement provides beneficial effects from protection of kidney against acute injury, promotion of kidney regeneration, retardation of CKD progression, and amelioration of extrarenal complications. Klotho also improves mineral metabolism disturbances and directly or indirectly lessens end organ dysfunction or abnormalities of advanced CKD. CKD-MBD, CKD-mineral and bone disorder; Ca, calcium; 1,25-D3, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D; Pi, phosphate.
