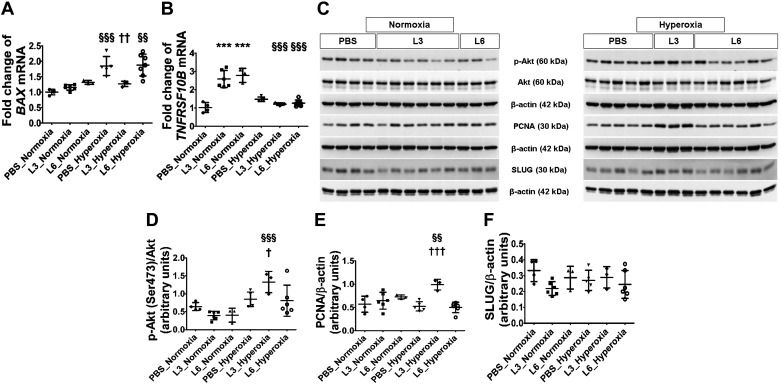
Fig. 6.
Apoptosis and cell proliferation indices in the lungs of C57BL/6J wild-type mice exposed to LPS and hyperoxia during the saccular phase of lung development. C57BL/6J wild-type mice were exposed to 21% O2 (normoxia) or 70% O2 (hyperoxia) during postnatal days (PNDs) 1–5 and injected intraperitoneally with 3 (L3) or 6 (L6) mg/kg of LPS or the vehicle (PBS) on PNDs 3–5. Whole-lung tissues were harvested on PND 14 for real-time RT-PCR and immunoblot analyses. Real-time RT-PCR analysis-based determination of BAX (A) and TNFRSF10B (B) mRNA expression. C: immunoblot determination of p-Akt, Akt, PCNA, SLUG, and β-actin protein levels. Quantification and normalization of p-Akt (D) band intensity to Akt, and PCNA (E) and SLUG (F) band intensities to β-actin. Values are expressed as means ± SD (n = 3–7 mice/group). Significant differences between PBS- and LPS-treated mice are indicated by ***P < 0.001 under normoxic conditions and by †P < 0.05, ††P < 0.01, and †††P < 0.001 under hyperoxic conditions. Significant differences between treatment-matched mice under normoxic and hyperoxic conditions are indicated by §§P < 0.01 and §§§P < 0.001.