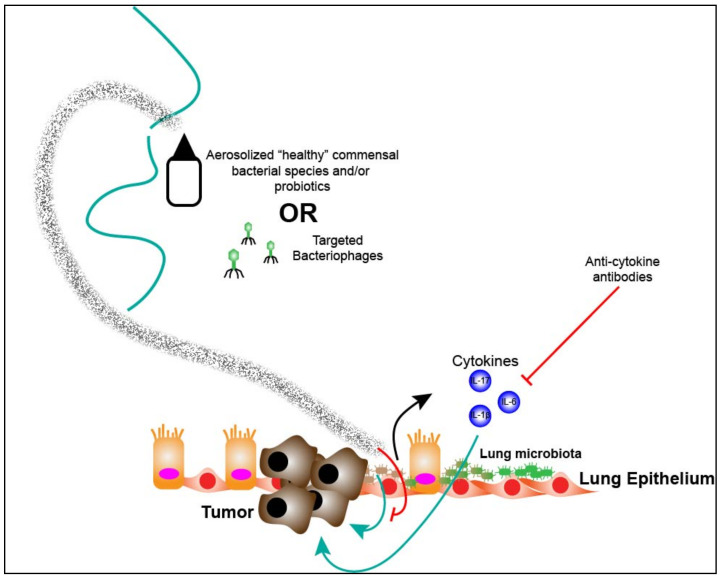
Figure 3.
Targeting the lung microbiome. Aerosolization of “healthy” commensal respiratory bacteria, probiotics or bacteriophages targeted against dysbiotic bacteria in the lung could disrupt pathogenic lung dysbiosis in lung cancer patients and lead to anti-tumorigenic effects. Immunologic downstream effects of lung dysbiosis in lung cancer patients could lead to the use of specific anti-cytokine antibodies to modulate the inflammatory milieu promoting a more anti-tumorigenic tumor microenvironment within the lung.