Fig. 1.
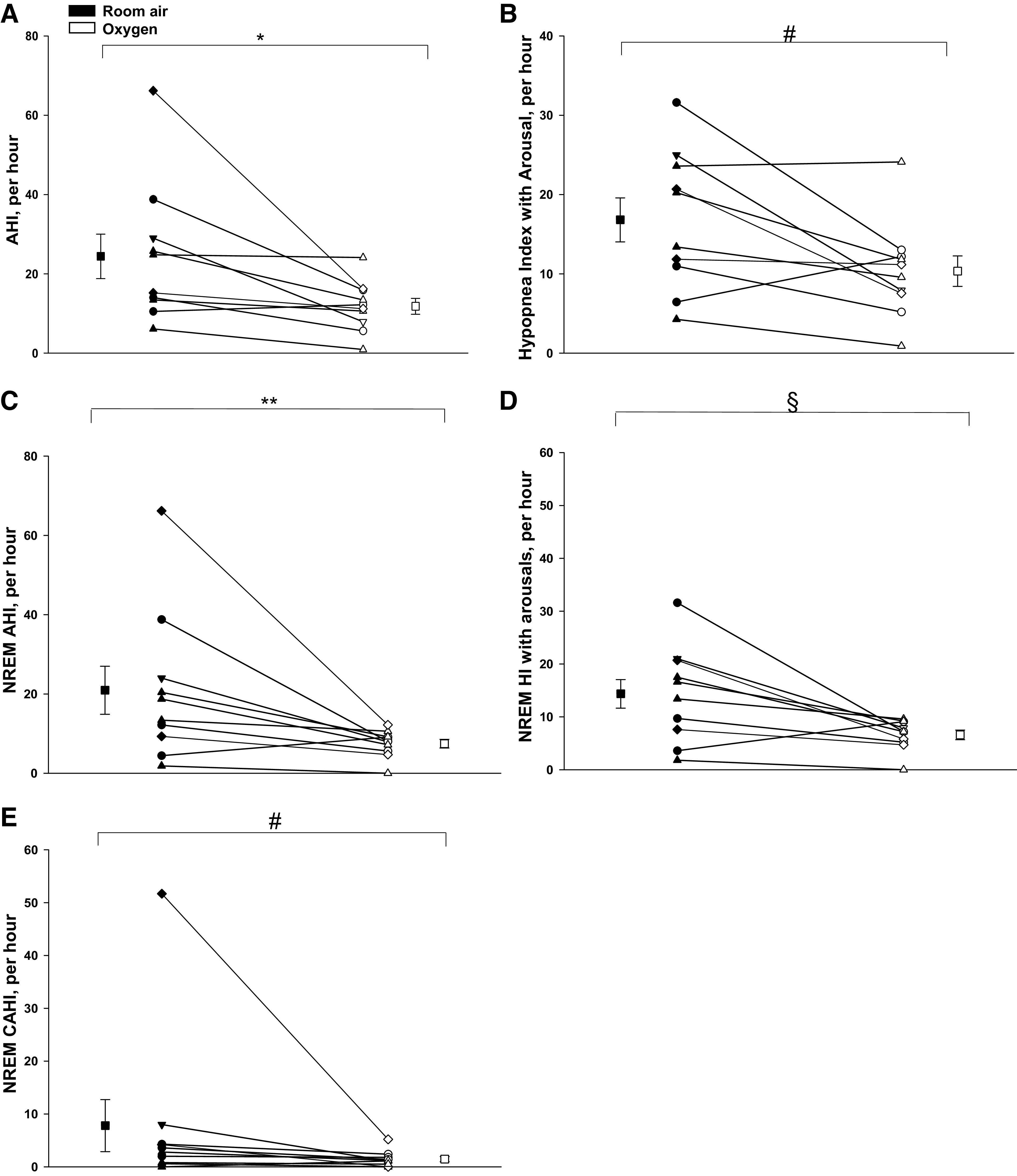
A: the apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) under conditions of room air and Oxy (supplemental oxygen). There was a significant decline in the mean AHI with Oxy vs. room air, *P = 0.006. B: the hypopnea index (HI) with arousals alone under conditions of room air and Oxy. There was a significant decline in the mean HI scored with arousals alone with Oxy versus room air, #P = 0.03. C: non-rapid eye movement (NREM) AHI under conditions of room air and Oxy. There was a significant decline in the NREM AHI during Oxy versus room air, **P = 0.01. D: NREM HI scored with arousals alone under conditions room air and Oxy, which declined significantly with Oxy versus room air, §P = 0.02. Individual and means (±SE) data are presented in all four figures, where black and white symbols represent room air and Oxy trials, respectively; h, hour. E: NREM central apnea-hypopnea index (CAHI) scored with arousals alone under conditions room air and Oxy, which declined significantly with Oxy versus room air, #P = 0.01 (also see Table 1). Individual and means (±SE) data are presented in all five figures, where black and white symbols represent room air and Oxy trials, respectively; h, hour.
