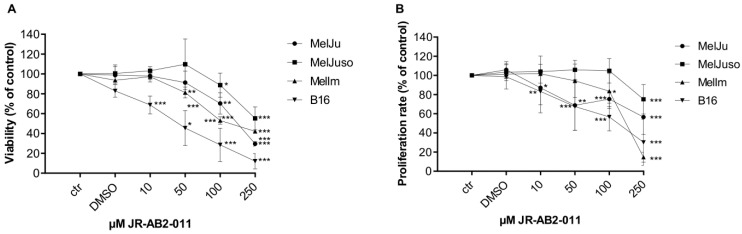
Figure 1.
Inhibition of mTORC2 reduced cell viability and proliferation dose-dependently. (A) The dose-dependent toxic effect of JR-AB2-011 (10–250 µM) was assessed by 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazoliumbromid (MTT) assay over 48 h in human and murine melanoma cells. Viability was plotted relative to untreated controls set to 100% (± standard deviation (SD) of three independent experiments). (B) bromdesoxyuridin BrdU incorporation assay indicates relevant inhibition of proliferation in human and murine melanoma cells by JR-AB2-011 (10–250 µM) after 48 h compared with the loss of cells in MTT assay. Treatment was normalized to untreated controls (± SD of three independent experiments). Asterisks (* p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.001) indicate significance between treatment and the control.