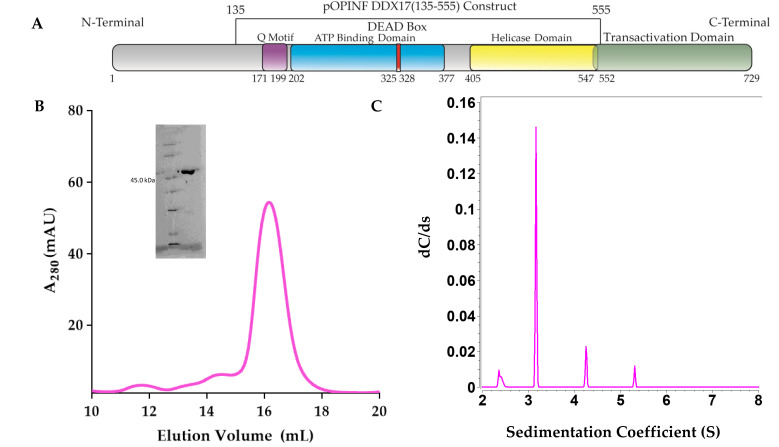
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic representation of DDX17 highlighting individual domains. DDX17135–555, which contains the Q motif, ATP binding domain, DEAD-box, and the helicase domain, was used in downstream studies. (B) The chromatogram from the size exclusion purification (Superdex 200 Increase gl 10/300) of DDX17135–555, suggesting that DDX17(135–555) can be purified to ~68% homogeneity (~16 mL). The y-axis represents absorbance at 260 nm while the x-axis represents elution volume. We collected peak fractions from 15.5 to 16.5 mL for subsequent analysis. The inset to Figure 1B represents the SDS-PAGE analysis of DDX17135–555 (48.45 kDa) following size exclusion chromatography. (C) Sedimentation coefficient distribution of DDX17135–555 obtained from analytical ultracentrifugation sedimentation velocity (SV-AUC) experiment. The peak at ~3.16S represents monodispersed DDX17135–555. Sedimentation coefficient values are corrected to standard solvent conditions (20 °C in water).