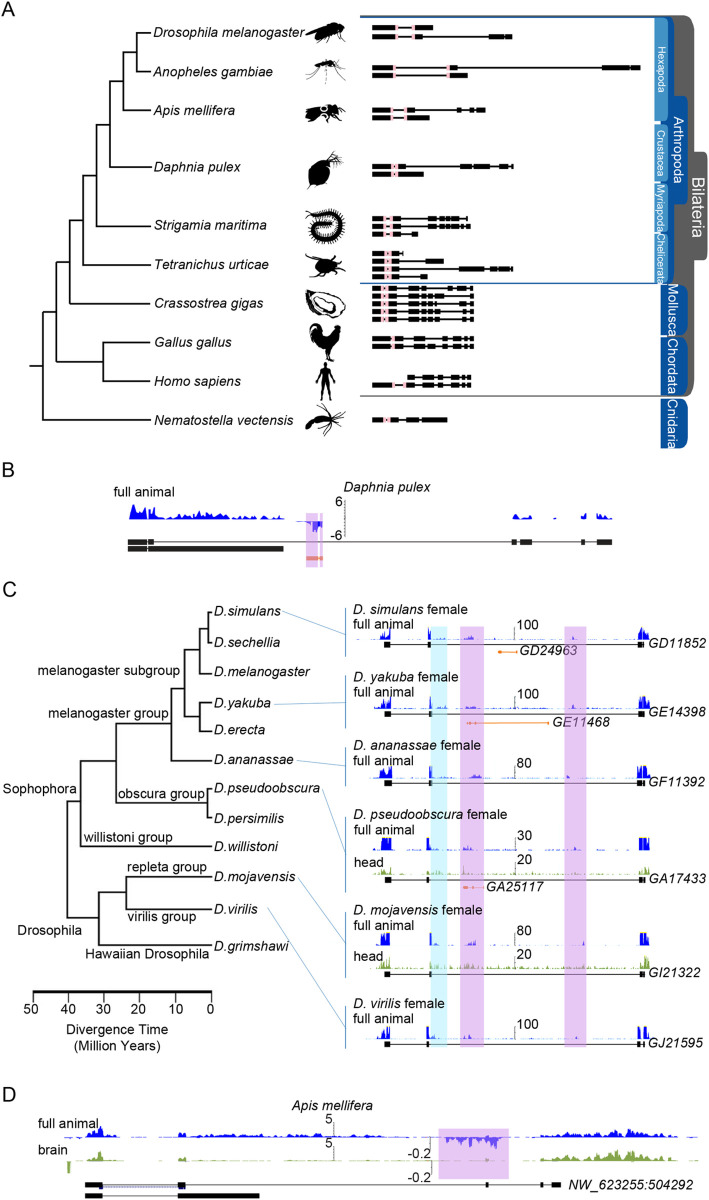
Fig 5. Evolutionary conservation of bs and bsAS.
(A) Annotation of bs isoforms along metazoans. bs orthologous genes were manually annotated taking advantage of available RNA-Seq data in all species depicted. The pink box represents the MADS box, conserved along evolution. (B) Expression of bs and bsAS in Daphnia pulex. An antisense transcript is detected within the long intron of bs gene. (C) Expression of bs and bsAS in Drosophila species. Unstranded RNA-Seq tracks from modENCODE project are shown. When available, whole animals (in blue) and heads (in green) RNA-Seq samples have been represented. The long isoform of bs is annotated in all species. We have been able to identify reads likely corresponding to the short isoform of bs (highlighted in blue). D. simulans, D. yakuba and D. pseudoobscura also present annotated antisense genes embedded into the long intron of the coding gene (in orange). In all species, reads corresponding to the bsAS gene have been identified (in purple). (D) Expression of bs and bsAS in A. mellifera whole animals (in blue) and brains (in green). As in fly, bs and bsAS are less expressed in brains compared to whole animals.