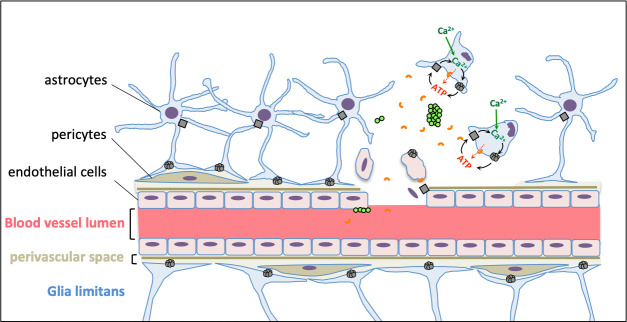
Fig 7. Role of aCx43 in astrocyte targeting by Ply and PN meningitis.
Astrocytes regulate the BBB function through their end-feet contacting blood vessels. The BBB is represented with major cell types of the vascular unit and the different endothelial, perivascular space and glia limitans compartments. Crossing of the BBB by PN is associated with the destabilization of blood vessels seals. Secreted Ply induces the release of ATP (red arrow) in the extracellular space by forming small pores or “arcs” in the plasma membrane of astrocytes (orange half circles). Black arrows: ATP stimulates Ca2+ signaling via purinergic receptors (grey box). Increase cytosolic Ca2+ activates the opening of Cx43 hemichannels (grey circles) further amplifying ATP release and cytosolic Ca2+ increase, resulting in the destruction of astrocytic processes, plasma membrane permeabilization and eventually astrocytic death linked to Ca2+ influx (green arrow) and overload. Disruption of astrocyte-endothelial cells regulation destabilizes the BBB, favoring PN translocation and growth in the brain cortex due to local perfusion of blood vessel luminal content.