Figure 4.
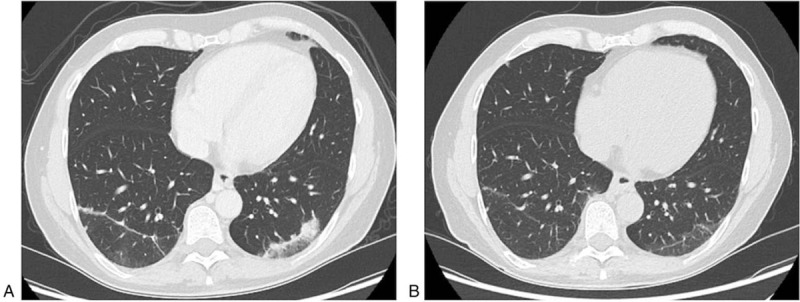
Axial contrast-enhanced CT-scans of a 50-year-old male patient (#3) with a non-functional NET G2 of the pancreatic tail, who developed pneumonitis during treatment with pembrolizumab. Axial contrast-enhanced CT-scan of the chest reveals disseminated bilateral ground glass opacities suggesting pneumonitis after several cycles of treatment with pembrolizumab in October 2018 (a). Axial contrast-enhanced CT-scan in December 2018 demonstrates regression of the ground glass opacities after initiation of treatment with adalimumab therapy and discontinuation of pembrolizumab therapy (b).
