FIGURE 2.
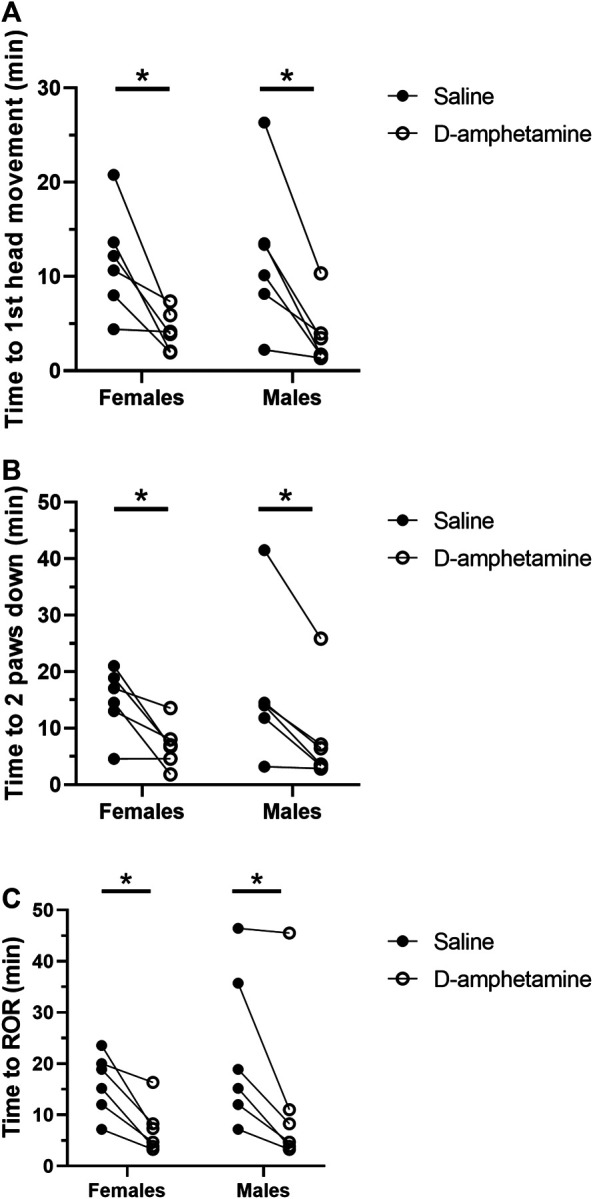
D-amphetamine (3 mg/kg, IV) hastens the recovery time for behavioral endpoints correlating with return of consciousness after fentanyl (55 µg/kg, IV). (A) Time to first head movement. A two-way mixed factor ANOVA and Bonferroni’s post hoc analysis revealed that d-amphetamine decreased time to first head movement significantly in females (t (6) = 3.370, p = 0.0142) and males (t (10) = 3.892, p = 0.0060). (B) Time to the return of two paws to the ground. A two-way mixed factor ANOVA and Bonferroni’s post hoc analysis revealed that d-amphetamine significantly decreased time to two paws down in females (t (10) = 3.553, p = 0.0105) and males (t (10) = 3.761, p = 0.0074). (C) Time to return of righting. A two-way mixed factor ANOVA and Bonferroni’s post hoc analysis revealed that d-amphetamine significantly decreased time to ROR in females (t (10) = 3.191, p = 0.0193) and males (t (10) = 3.536, p = 0.0108). *p < 0.05, n = 12 rats.
