Figure 2. Help-centric therapeutic avenues.
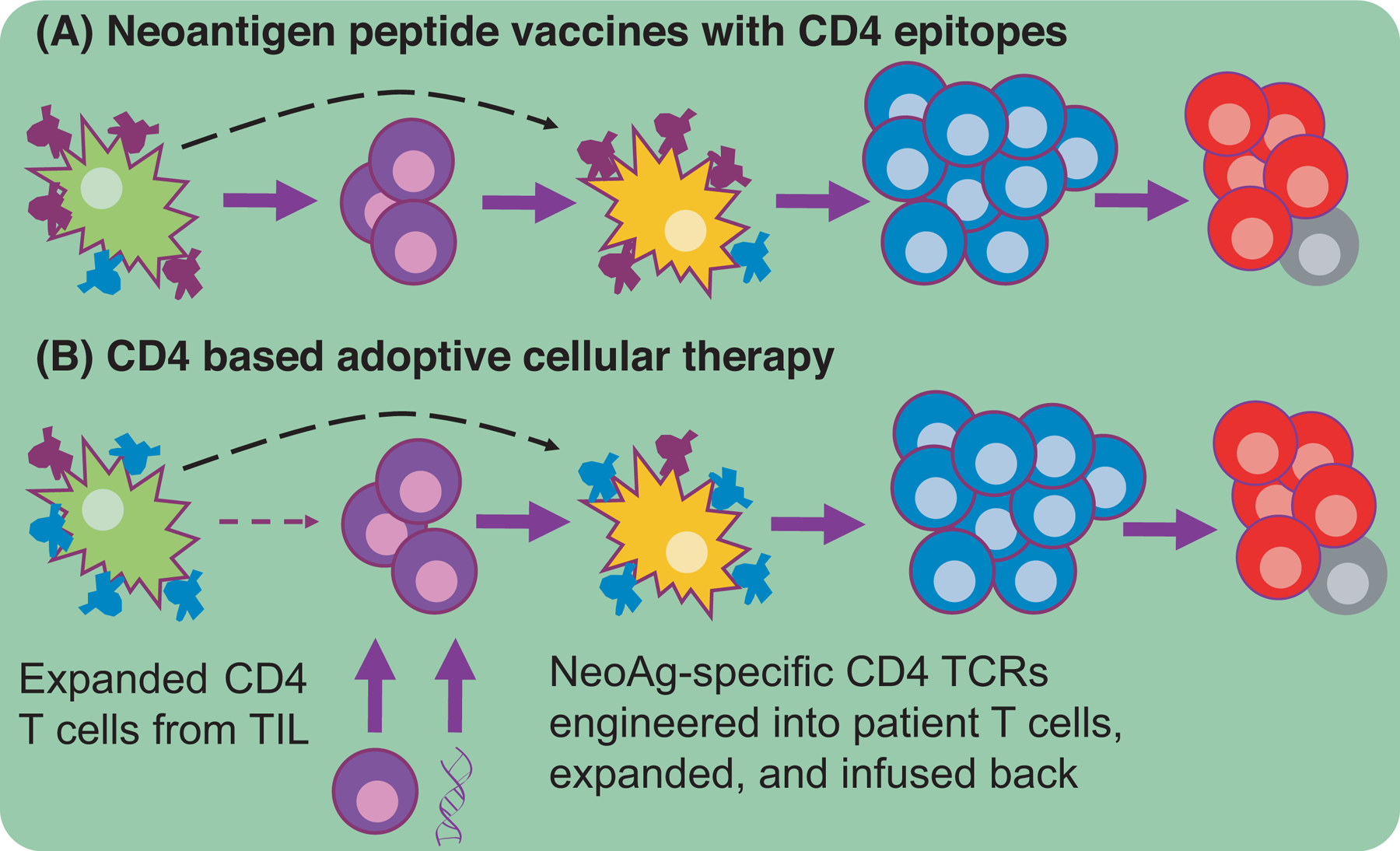
A major issue with anti-tumor immunity is the paucity of NeoAgs available for cross-presentation. (A) Peptide vaccines containing CD4-NeoAg epitopes (purple) increase the amount of NeoAg migratory DCs carry to LNs where activated CD4+ T cells will subsequently result in LN-resident DC conditioning, proper CTL priming, robust CTL expansion, and memory formation. (B) An alternative therapeutic modality functions via the expansion of CD4+ T cells found in the TIL of a patient or the genetic introduction of NeoAg-specificity. Both ACT strategies circumscribe the need for migratory DC to carry NeoAgs to the LN. The expanded helper cells will presumably condition the resident DC and ultimately lead to polyfunctional CTLs.
