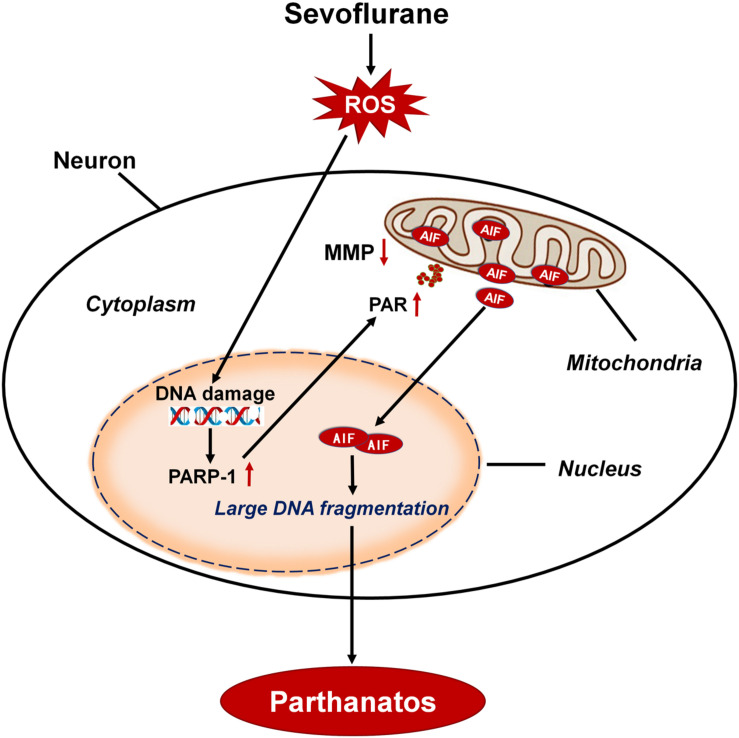
FIGURE 11.
Schematic demonstrating the role of oxidative DNA damage in sevoflurane-induced neuronal cell Parthanatos. In the developing brain, sevoflurane exposure results in overproduction of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS). ROS-induced oxidative stress contributes to DNA damage, which is associated with neuronal cell death. Massive DNA damage initiates excessive PARP-1 activation and subsequent cytoplasmic PAP polymer accumulation which results in mitochondrial depolarization, leading to the AIF translocation from mitochondria to nucleus. Therefore, sevoflurane contributes to overproduction of ROS and resultant DNA damage, leading to PARP-1-dependent cell death (Parthanatos).