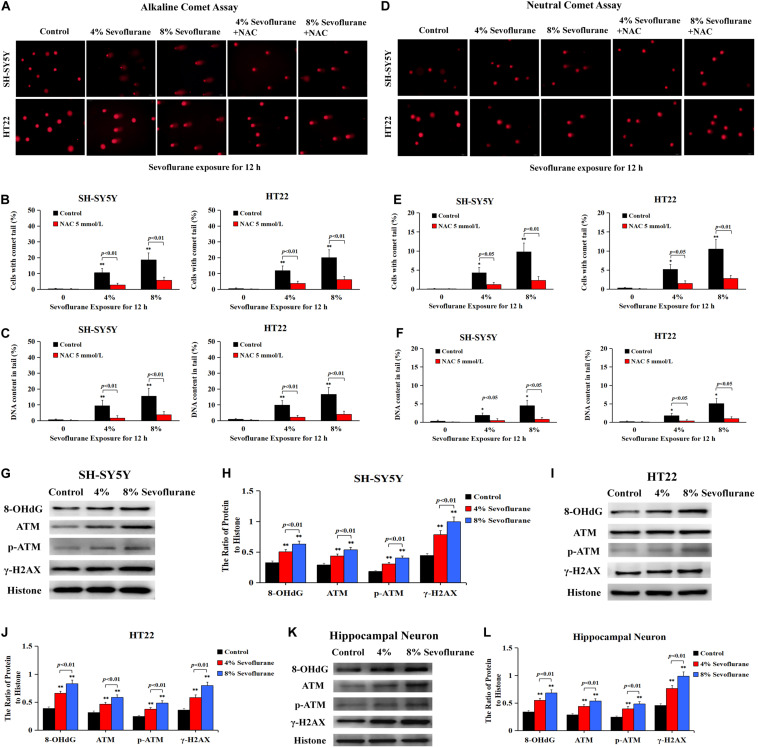
FIGURE 5.
Sevoflurane induced DNA damage in neuronal cells. (A) Images of neuronal cells acquired from fluorescence microscopy after alkaline comet assay. SH-SY5Y cells and HT22 cells treated with 4 and 8% sevoflurane for 12 h showed more cells with comet tails than that in control group, and the higher concentration, the longer the comet tails. Pretreatment of neuronal cells with antioxidant NAC at 5 mmol/L markedly prevented sevoflurane-induced appearance of comet tails in SH-SY5Y cells and HT22 cells. (B,C) Statistical analysis of alkaline comet assay revealed that sevoflurane induced a significant increase in the percentage of cells with comet tails and DNA content within the tails (p < 0.01), which were markedly inhibited in the presence of NAC (p < 0.01). (D) Images of neuronal cells acquired from fluorescence microscopy after neutral comet assay. Compared with the control group, SH-SY5Y cells and HT22 cells treated with 4 and 8% sevoflurane for 12 h presented longer comet tails, in a concentration-dependent manner. However, the appearance of comet tails in SH-SY5Y cells and HT22 cells caused by sevoflurane were obviously prevented by pretreatment of NAC. (E,F) Statistical analysis of neutral comet assay demonstrated that sevoflurane induced a significant increase in the percentage of cells with comet tails and DNA content within the tails (p < 0.05, p < 0.01), which were markedly reversed by pretreatment of NAC (p < 0.05, p < 0.01). (G–L) Western blotting and quantitative analysis showed that 4 and 8% sevoflurane for 12 h concentration-dependently induced upregulation of DNA damage-related protein 8-OHdG, γH2AX, and p-ATM in SH-SY5Y cells, HT22 cells, and hippocampal neurons (p < 0.01). Compared with the control group, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01. Data are represented as mean ± SD from five independent experiments.