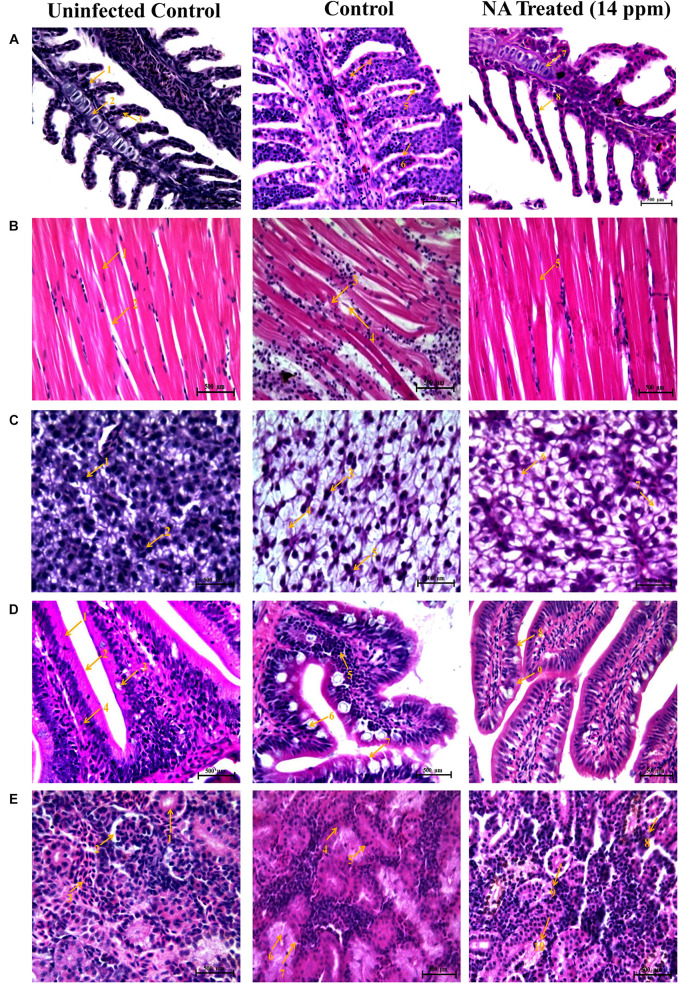
FIGURE 10.
Histopathology analysis of gills (A). 1. Branchial blood vessels; 2. Primary lamella; 3. Secondary lamella; 4. Fusion of secondary lamella; 5. Lamellar lifting; 6. Proliferation of filamentary epithelium; 7. Normal branchial blood vessels; 8. Rescued & healthy secondary lamellae. Histopathology analysis of muscle (B). 1. Muscle bundles; 2. Muscle fiber; 3. Degeneration of muscle bundles; 4. Swelling of muscle fiber; 5. Healthy muscle bundles. Histopathology analysis of liver (C). 1. Hepatocytes; 2. Spherical nucleus; 3. Fatty acid changes in hepatocytes; 4. Cytoplasmic vacuolation; 5. Hepatocytes disruption; 6. Rescued and healthy hepatocytes; 7. Small cytoplasmic vacuolation. Histopathology analysis of intestine (D). 1. Tunica mucosa; 2. External muscle layer; 3. Goblet cell; 4. Lymphocytes; 5. Degeneration of epithelial cells; 6. Hyperplasia of goblet cells; 7. Collapsed tunica mucosa; 8. Normal goblet cell; 9. Rescued and healthy tunica mucosa. Histopathology analysis of kidney (E). 1. Renal glomerulus; 2. Bowman’s space; 3. Normal distal tubules; 4. Congested distal tubules; 5. Hematopoietic necrosis; 6. Degeneration of renal glomerulus; 7. Reduced bowman’s space; 8. Normal bowman’s space; 9. Normal renal glomerulus; 10. Rescued and healthy distal tubulus.