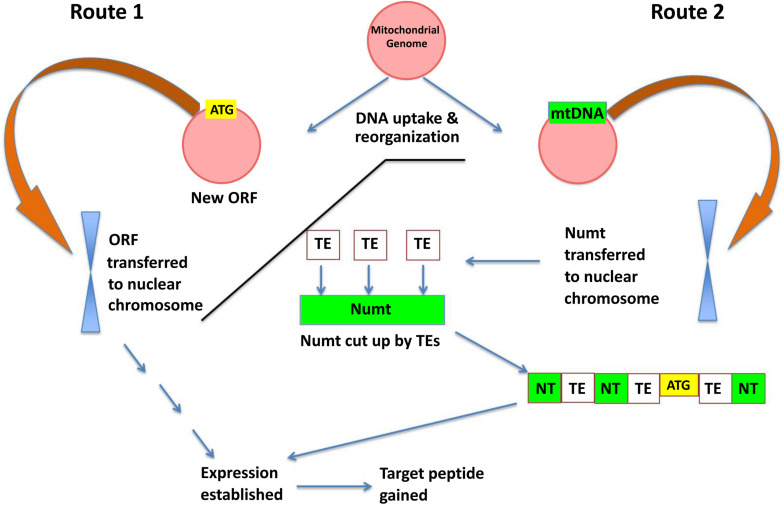
FIGURE 6.
A model for orphan gene evolution through the mitochondrial genome. Novel sequences are created due to the high rearrangement rate in the mitochondrial genome, and then inserted into a nuclear chromosome. The transferred DNA may already contain gene coding information like KNIT (left side of model: Route 1) or may obtain an open reading frame via other genome mechanisms such as transposon transposition (right side: Route 2).