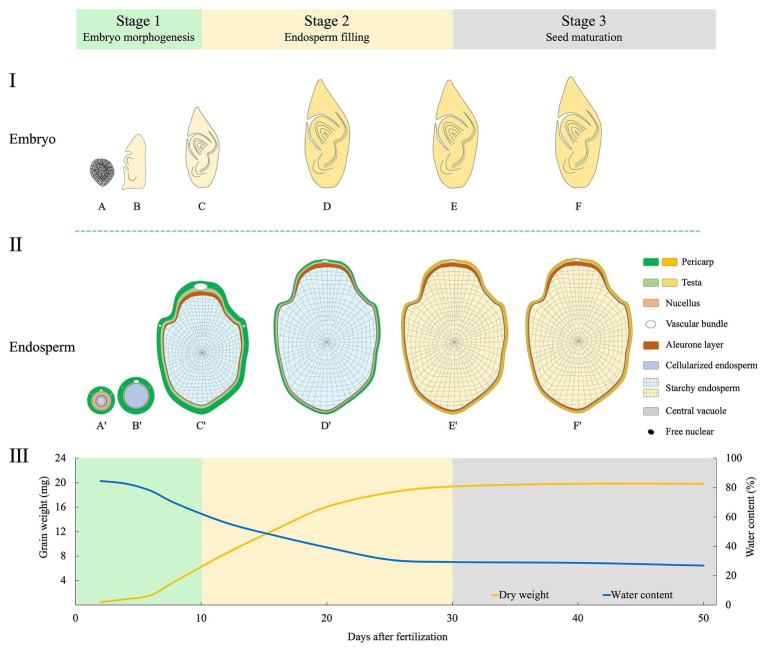
Figure 2.
Schematic illustration of morphological changes of embryo (longitudinal section, I), endosperm (transversal, II), and the dynamics of dry matter accumulation (III) during rice grain filling. The three phases proposed are indicated. Changed colors of the pericarp and testa show the process of degradation of maternal tissues (Wu et al., 2016a,b), and that of the starchy endosperm indicates the grain-filling process. The curve of grain weight and water content are depicted by data synthesized from Zhu et al. (2011), Fu et al. (2013), and Wu et al. (2016b). Stage 1 (embryo morphogenesis): At 2 days after fertilization (DAF), embryo is at globular stage (A), and endosperm at the coenocyte stage (A'). At 5 DAF, embryo has the first leaf primordium and recognizable scutellum (B), endosperm cellularization is completed (B'). At 10 DAF, embryo morphogenesis is basically completed (C); endosperm differentiation is finished, with two structures of the aleurone and starchy endosperm (C'). Stage 2 (endosperm filling): During 10–30 DAF, embryo becomes dormant (D,E); endosperm accumulates storage compounds and attains its maximum weight (D',E'). Stage 3 (seed maturation): embryo (F) and endosperm (F') continue to dehydrate until maturity.