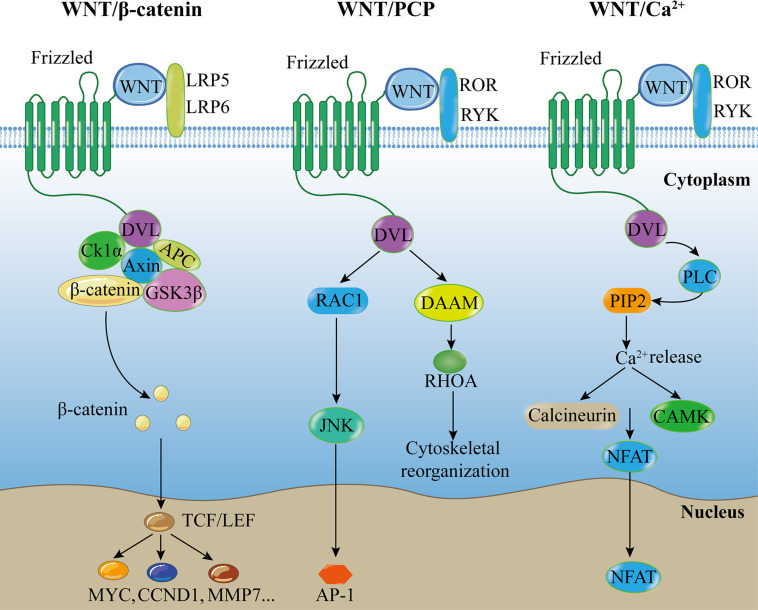
FIGURE 1.
Canonical and non-canonical WNT pathways. Canonical WNT pathway: Extracellular WNT ligands bind to FZD and LRP5/6 on the cell membrane, and recruit DVL protein to promote dissociation of the β-catenin destruction complex, followed by accumulation of β-catenin, which translocates to the nucleus to interact with target downstream signaling molecules, activating intracellular signaling cascades. WNT/PCP pathway: Extracellular non-canonical WNT ligands bind to FZD receptor and/or ROR/RYK co-receptors at the cell membrane, and recruit DVL protein to promote downstream effector components, such as RAC and RHOA signaling cascades, regulating tissue polarity and cell movement. WNT/Ca2+ pathway: Extracellular WNT ligands bind to FZD receptor and/or ROR/RYK co-receptors at the cell membrane, and recruit DVL protein to promote PLC, leading to the formation of IP3 and DAG from PIP2, resulting in intracellular Ca2+ accumulation. Ca2+ can activate CAMK and NFAT transcription factor to regulate downstream cascades. Abbreviations: PCP, planar cell polarity; LRP, low-density lipoprotein receptor-related proteins; ROR, receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor; RYK, receptor-like tyrosine kinase; DVL, disheveled; CK1α, Casein Kinase-1α; APC, adenomatous polyposis coli; GSK3β, glycogen synthase kinase-3β; DAAM, disheveled associated activator of morphogenesis; PLC, phospholipase C; PIP2, phospholipid phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; JNK, Jun-N-terminal kinase; RHOA, ras homolog family member A; CAMK, calmodulin-dependent protein kinase; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T cells; TCF/LEF, T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor; CCND1, Cyclin D1; MMP7, matrix metallopeptidase 7; AP-1, activator protein 1.