Figure 4.
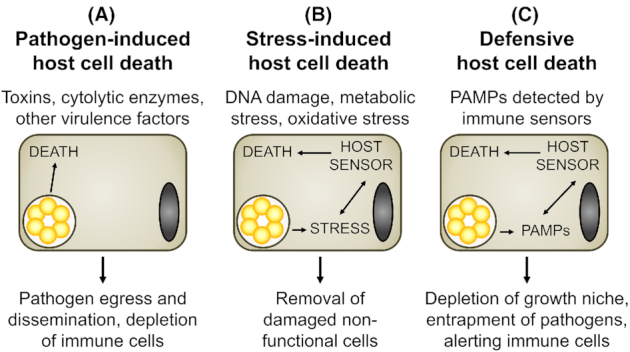
The various roles of infection-associated cell death. (A) Host cell death can be triggered by the pathogen, for instance to mediate pathogen release, spread to deeper tissue layers, or immune cell depletion. (B) Host cell death may be triggered by the host cell itself as response to non-compensable infection-induced stress, such as DNA damage, oxidative stress or metabolic stress. (C) Upon detection of an invading pathogen by immune sensors, host cells may trigger cell death as defense response. Note that immune mediators, such as cytotoxic cytokines and immune cell-mediated killing mechanisms, can promote host cell death either by inducing cellular stress (B) or by supporting death-inducing host cell-intrinsic defense responses (C).
