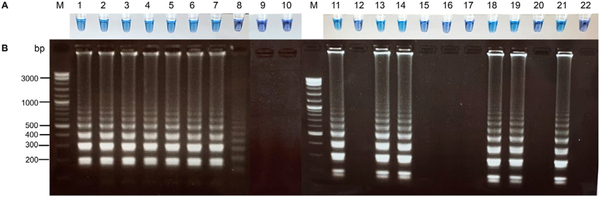
Figure 2.
Specificity testing of the RT-LAMP assay for the detection of HCV. (A) Visual detection of RT-LAMP products by pre-adding HNB. A color change from purple to sky blue was only observed in tubes containing specific HCV genomes, whereas negative samples were purple. (B) Electrophoresis pattern of the RT-LAMP products in the same order as in panel A. The results showed the presence of typical ladder-like banding patterns in HCV samples, but the absence of a banding pattern in HIV samples, HBV samples, and negative controls. M = 1 kb marker; 1 = HCV 1b; 2 = HCV 3a; 3 = HCV 6; 4 = HCV 6; 5 = HCV 6; 6 = HCV 1a; 7 = PC; 8 = NTC; 9, 10 = healthy blood donors; 11 = HCV 1b; 12 = HBV; 13 = HCV 1a; 14 = HCV 1b; 15 = HIV; 16 = HCV 1a (viral load = 3163 IU/mL); 17 = HBV; 18 = HCV 1b; 19 = HCV 6; 20 = HIV; 21 = PC; 22 = NTC. (HCV, hepatitis C virus; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; HBV, hepatitis B virus; PC, positive control; NTC, no template control).